Influence of hypoxia and neoangiogenesis on the growth of pancreatic cancer
- PMID: 12605718
- PMCID: PMC150383
- DOI: 10.1186/1476-4598-2-12
Influence of hypoxia and neoangiogenesis on the growth of pancreatic cancer
Abstract
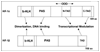
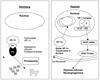
As with other solid tumors, the growth and metastasis of pancreatic cancer is critically dependent on tumor angiogenesis. A major stimulus for a tumor's recruitment of additional blood vessels is cellular hypoxia, a condition which is especially pronounced in this neoplasm. Hypoxia induces transcriptional activation of genes that alter cellular metabolism and promote neoangiogenesis. Pancreatic cancer cells have demonstrated activation of such adaptive pathways even in the absence of hypoxia. A highly-angiogenic response in this neoplasm correlates with increased tumor growth, increased metastasis, and decreased survival. Pancreatic cancers expressing high levels of vascular endothelial growth factor, a potent pro-angiogenic cytokine, also have a higher incidence of metastasis and poorer prognosis. Pancreatic cancer cells uniquely express receptors for vascular endothelial growth factor, indicating a role for an autocrine loop in tumor proliferation and invasion. Multiple experimental anti-angiogenic strategies, many of which target vascular endothelial growth factor, reduce pancreatic cancer growth, spread, and angiogenesis. Anti-angiogenic treatments for pancreatic cancer will likely be most effective when used as an integral part of a combination chemotherapeutic regimen.
Figures
References
-
- Jemal A, Thomas A, Murray T, Thun M. Cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin. 2002;52:23–47. - PubMed
-
- Folkman J. Tumor angiogenesis: therapeutic implications. N Engl J Med. 1971;285:1182–1186. - PubMed
-
- O'Reilly MS, Boehm T, Shing Y, Fukai N, Vasios G, Lane WS, Flynn E, Birkhead JR, Olsen BR, Folkman J. Endostatin: an endogenous inhibitor of angiogenesis and tumor growth. Cell. 1997;88:277–285. - PubMed
-
- Moscatelli D, Presta M, Joseph-Silverstein J, Rifkin DB. Both normal and tumor cells produce basic fibroblast growth factor. J Cell Physiol. 1986;129:273–276. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

