The human chromokinesin Kid is a plus end-directed microtubule-based motor
- PMID: 12606572
- PMCID: PMC150335
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/cdg102
The human chromokinesin Kid is a plus end-directed microtubule-based motor
Abstract
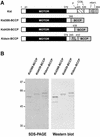
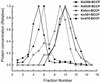
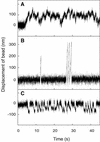
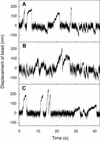
Kid is a kinesin-like DNA-binding protein known to be involved in chromosome movement during mitosis, although its actual motor function has not been demonstrated. Here, we describe the initial characterization of Kid as a microtubule-based motor using optical trapping microscopy. A bacterially expressed fusion protein consisting of a truncated Kid fragment (amino acids 1-388 or 1-439) is indeed an active microtubule motor with an average speed of approximately 160 nm/s, and the polarity of movement is plus end directed. We could not detect processive movement of either monomeric Kid or dimerizing chimeric Kid; however, low levels of processivity (a few steps) cannot be detected with our method. These results are consistent with Kid having a role in chromosome congression in vivo, where it would be responsible for the polar ejection forces acting on the chromosome arms.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The second microtubule-binding site of monomeric kid enhances the microtubule affinity.J Biol Chem. 2003 Jun 20;278(25):22460-5. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M212274200. Epub 2003 Apr 12. J Biol Chem. 2003. PMID: 12692123
-
Chromokinesin Kid and kinetochore kinesin CENP-E differentially support chromosome congression without end-on attachment to microtubules.Nat Commun. 2015 Mar 6;6:6447. doi: 10.1038/ncomms7447. Nat Commun. 2015. PMID: 25743205
-
The microtubule-binding and coiled-coil domains of Kid are required to turn off the polar ejection force at anaphase.J Cell Sci. 2016 Oct 1;129(19):3609-3619. doi: 10.1242/jcs.189969. Epub 2016 Aug 22. J Cell Sci. 2016. PMID: 27550518
-
Structural links to kinesin directionality and movement.Nat Struct Biol. 2000 Jun;7(6):456-60. doi: 10.1038/75850. Nat Struct Biol. 2000. PMID: 10881190 Review.
-
Subunits interactions in kinesin motors.Eur J Cell Biol. 2007 Sep;86(9):559-68. doi: 10.1016/j.ejcb.2007.05.008. Epub 2007 Jul 12. Eur J Cell Biol. 2007. PMID: 17628208 Review.
Cited by
-
Recurrent dominant mutations affecting two adjacent residues in the motor domain of the monomeric kinesin KIF22 result in skeletal dysplasia and joint laxity.Am J Hum Genet. 2011 Dec 9;89(6):767-72. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2011.10.016. Am J Hum Genet. 2011. PMID: 22152678 Free PMC article.
-
The HhH2/NDD domain of the Drosophila Nod chromokinesin-like protein is required for binding to chromosomes in the oocyte nucleus.Genetics. 2005 Dec;171(4):1823-35. doi: 10.1534/genetics.105.047464. Epub 2005 Sep 2. Genetics. 2005. PMID: 16143607 Free PMC article.
-
PinX1 is recruited to the mitotic chromosome periphery by Nucleolin and facilitates chromosome congression.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2009 Jun 19;384(1):76-81. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2009.04.077. Epub 2009 Apr 23. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2009. PMID: 19393617 Free PMC article.
-
How kinesin motor proteins drive mitotic spindle function: Lessons from molecular assays.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2010 May;21(3):260-8. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2010.01.018. Epub 2010 Jan 28. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2010. PMID: 20109570 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anchoring geometry is a significant factor in determining the direction of kinesin-14 motility on microtubules.Sci Rep. 2022 Sep 14;12(1):15417. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-19589-4. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 36104376 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Afshar K., Barton,N.R., Hawley,R.S. and Goldstein,L.S. (1995b) DNA binding and meiotic chromosomal localization of the Drosophila nod kinesin-like protein. Cell, 81, 129–138. - PubMed
-
- Antonio C., Ferby,I., Wilhelm,H., Jones,M., Karsenti,E., Nebreda,A.R. and Vernos,I. (2000) Xkid, a chromokinesin required for chromosome alignment on the metaphase plate. Cell, 102, 425–435. - PubMed
-
- Berliner E., Mahtani,H.K., Karki,S., Chu,L.F., Cronan,J.E. and Gelles,J.,Jr (1994) Microtubule movement by a biotinated kinesin bound to streptavidin-coated surface. J. Biol. Chem., 269, 8610–8615. - PubMed
-
- Chandra R., Salmon,E.D., Erickson,H.P., Lockhart,A. and Endow,S.A. (1993) Structural and functional domains of the Drosophila ncd microtubule motor protein. J. Biol. Chem., 268, 9005–9013. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

