A global representation of the protein fold space
- PMID: 12606708
- PMCID: PMC151350
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2628030100
A global representation of the protein fold space
Abstract
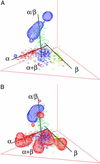
One of the principal goals of the structural genomics initiative is to identify the total repertoire of protein folds and obtain a global view of the "protein structure universe." Here, we present a 3D map of the protein fold space in which structurally related folds are represented by spatially adjacent points. Such a representation reveals a high-level organization of the fold space that is intuitively interpretable. The shape of the fold space and the overall distribution of the folds are defined by three dominant trends: secondary structure class, chain topology, and protein domain size. Random coil-like structures of small proteins and peptides are mapped to a region where the three trends converge, offering an interesting perspective on both the demography of fold space and the evolution of protein structures.
Figures



References
-
- Richardson J S. Adv Protein Chem. 1981;34:167–339. - PubMed
-
- Chothia C. Nature. 1992;357:543–544. - PubMed
-
- Zhang C, DeLisi C. J Mol Biol. 1998;284:1301–1305. - PubMed
-
- Kim S H. Nat Struct Biol. 1998;5,Suppl.:643–645. - PubMed
-
- Sanchez R, Pieper U, Melo F, Eswar N, Marti-Renom M A, Madhusudhan M S, Mirkovic N, Sali A. Nat Struct Biol. 2000;7,Suppl.:986–990. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

