Integrin beta cytoplasmic domain interactions with phosphotyrosine-binding domains: a structural prototype for diversity in integrin signaling
- PMID: 12606711
- PMCID: PMC151330
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.262791999
Integrin beta cytoplasmic domain interactions with phosphotyrosine-binding domains: a structural prototype for diversity in integrin signaling
Abstract
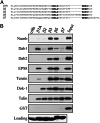
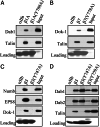
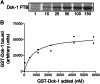
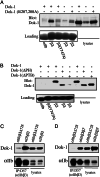
The cytoplasmic domains (tails) of heterodimeric integrin adhesion receptors mediate integrins' biological functions by binding to cytoplasmic proteins. Most integrin beta tails contain one or two NPXYF motifs that can form beta turns. These motifs are part of a canonical recognition sequence for phosphotyrosine-binding (PTB) domains, protein modules that are present in a wide variety of signaling and cytoskeletal proteins. Indeed, talin and ICAP1-alpha bind to integrin beta tails by means of a PTB domain-NPXY ligand interaction. To assess the generality of this interaction we examined the binding of a series of recombinant PTB domains to a panel of short integrin beta tails. In addition to the known integrin-binding proteins, we found that Numb (a negative regulator of Notch signaling) and Dok-1 (a signaling adaptor involved in cell migration) and their isolated PTB domain bound to integrin tails. Furthermore, Dok-1 physically associated with integrin alpha IIb beta 3. Mutations of the integrin beta tails confirmed that these interactions are canonical PTB domain-ligand interactions. First, the interactions were blocked by mutation of an NPXY motif in the integrin tail. Second, integrin class-specific interactions were observed with the PTB domains of Dab, EPS8, and tensin. We used this specificity, and a molecular model of an integrin beta tail-PTB domain interaction to predict critical interacting residues. The importance of these residues was confirmed by generation of gain- and loss-of-function mutations in beta 7 and beta 3 tails. These data establish that short integrin beta tails interact with a large number of PTB domain-containing proteins through a structurally conserved mechanism.
Figures
References
-
- Hynes R O. Cell. 1987;48:549–554. - PubMed
-
- Liu S, Calderwood D A, Ginsberg M H. J Cell Sci. 2000;113:3563–3571. - PubMed
-
- Ulmer T S, Yaspan B, Ginsberg M H, Campbell I D. Biochemistry. 2001;40:7498–7508. - PubMed
-
- Trub T, Choi W E, Wolf G, Ottinger E, Chen Y, Weiss M, Shoelson S E. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:18205–18208. - PubMed
-
- Dans M, Gagnoux-Palacios L, Blaikie P, Klein S, Mariotti A, Giancotti F G. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:1494–1502. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

