Five components of the ethylene-response pathway identified in a screen for weak ethylene-insensitive mutants in Arabidopsis
- PMID: 12606727
- PMCID: PMC151454
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0438070100
Five components of the ethylene-response pathway identified in a screen for weak ethylene-insensitive mutants in Arabidopsis
Abstract
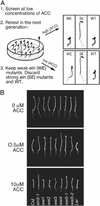
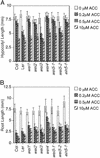
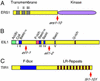
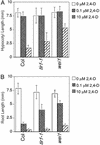
Five ethylene-insensitive loci (wei1-wei5) were identified by using a low-dose screen for "weak" ethylene-insensitive mutants. wei1, wei2, and wei3 seedlings showed hormone insensitivity only in roots, whereas wei4 and wei5 displayed insensitivity in both roots and hypocotyls. The genes corresponding to wei1, wei4, and wei5 were isolated using a positional cloning approach. The wei1 mutant harbored a recessive mutation in TIR1, which encodes a component of the SCF protein ubiquitin ligase involved in the auxin response. wei4, a dominant mutant, resulted from a mutation in the ethylene receptor ERS, whereas wei5, a semidominant mutant, was caused by a mutation in the EIN3-related transcription factor gene EIL1. The simultaneous loss of functional WEI5EIL1 and EIN3 nearly completely abolished the ethylene response in etiolated seedlings, and adult plants were highly susceptible to infection by the necrotrophic fungal pathogen Botrytis cinerea. Moreover, wei5eil1 ein3 double mutants were able to fully suppress constitutive signaling caused by ctr1, suggesting a synergistic interaction among these gene products. Unlike previously known root ethylene-insensitive mutants, wei2 and wei3 were not affected in their response to auxin and showed a normal response to gravity. Genetic mapping studies indicate that wei2 and wei3 correspond to previously unidentified ethylene pathway genes that may control cell-elongation processes functioning at the intersection of the ethylene and auxin response pathways.
Figures

References
-
- Abeles F, Morgan P, Saltveit M. Ethylene in Plant Biology. San Diego: Academic; 1992.
-
- Johnson P R, Ecker J R. Annu Rev Genet. 1998;32:227–254. - PubMed
-
- Bleecker A, Estelle M, Somerville C, Kende H. Science. 1988;241:1086–1089. - PubMed
-
- Kieber J J, Rothenberg M, Roman G, Feldmann K A, Ecker J R. Cell. 1993;72:427–441. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

