Paracellular ion channel at the tight junction
- PMID: 12609869
- PMCID: PMC1302736
- DOI: 10.1016/S0006-3495(03)74975-3
Paracellular ion channel at the tight junction
Abstract
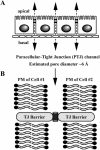
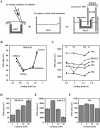
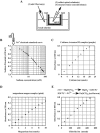
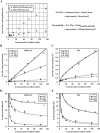
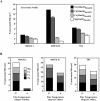
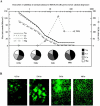
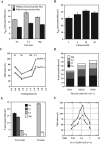
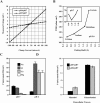
The tight junction of epithelial cells excludes macromolecules but allows permeation of ions. However, it is not clear whether this ion-conducting property is mediated by aqueous pores or by ion channels. To investigate the permeability properties of the tight junction, we have developed paracellular ion flux assays for four major extracellular ions, Na(+), Cl(-), Ca(2+), and Mg(2+). We found that the tight junction shares biophysical properties with conventional ion channels, including size and charge selectivity, dependency of permeability on ion concentration, competition between permeant molecules, anomalous mole-fraction effects, and sensitivity to pH. Our results support the hypothesis that discrete ion channels are present at the tight junction. Unlike conventional ion channels, which mediate ion transport across lipid bilayers, the tight junction channels must orient parallel to the plane of the plasma membranes to support paracellular ion movements. This new class of paracellular-tight junction channels (PTJC) facilitates the transport of ions between separate extracellular compartments.
Figures

References
-
- Balasubramanian, S., J. W. Lynch, and P. H. Barry. 1995. The permeation of organic cations through cAMP-gated channels in mammalian olfactory receptor neurons. J. Membr. Biol. 146:177–191. - PubMed
-
- Balasubramanian, S., J. W. Lynch, and P. H. Barry. 1997. Concentration dependence of sodium permeation and sodium ion interactions in the cyclic AMP-gated channels of mammalian olfactory receptor neurons. J. Membr. Biol. 159:41–52. - PubMed
-
- Barker, G., and N. L. Simmons. 1981. Identification of two strains of cultured canine renal epithelial cells (MDCK cells) which display entirely different physiological properties. Q. J. Exp. Physiol. 66:61–72. - PubMed
-
- Bell, C. L., and P. M. Quinton. 1992. T84 cells: anion selectivity demostrates expression of Cl− conductance affected in cystic fibrosis. Am. J. Physiol. 262:C555–C562. - PubMed
-
- Cereijido, M. 1984. Electrical properties of Madin-Darby canine kidney cells. Federation Proc. 43:2230–2235. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

