Direct activation of gastric H,K-ATPase by N-terminal protein kinase C phosphorylation. Comparison of the acute regulation mechanisms of H,K-ATPase and Na,K-ATPase
- PMID: 12609871
- PMCID: PMC1302738
- DOI: 10.1016/S0006-3495(03)74977-7
Direct activation of gastric H,K-ATPase by N-terminal protein kinase C phosphorylation. Comparison of the acute regulation mechanisms of H,K-ATPase and Na,K-ATPase
Abstract
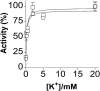
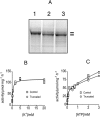
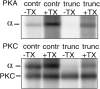
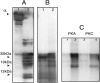
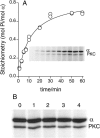
In this study we compared the protein kinase dependent regulation of gastric H,K-ATPase and Na,K-ATPase. The protein kinase A/protein kinase C (PKA/PKC) phosphorylation profile of H,K-ATPase was very similar to the one found in the Na,K-ATPase. PKC phosphorylation was taking place in the N-terminal part of the alpha-subunit with a stoichiometry of approximately 0.6 mol Pi/mole alpha-subunit. PKA phosphorylation was in the C-terminal part and required detergent, as is also found for the Na,K-ATPase. The stoichiometry of PKA-induced phosphorylation was approximately 0.7 mol Pi/mole alpha-subunit. Controlled proteolysis of the N-terminus abolished PKC phosphorylation of native H,K-ATPase. However, after detergent treatment additional C-terminal PKC sites became exposed located at the beginning of the M5M6 hairpin and at the cytoplasmic L89 loop close to the inner face of the plasma membrane. N-terminal PKC phosphorylation of native H,K-ATPase alpha-subunit was found to stimulate the maximal enzyme activity by 40-80% at saturating ATP, depending on pH. Thus, a direct modulation of enzyme activity by PKC phosphorylation could be demonstrated that may be additional to the well-known regulation of acid secretion by recruitment of H,K-ATPase to the apical membranes of the parietal cells. Moreover, a distinct difference in the regulation of H,K-ATPase and Na,K-ATPase is the apparent absence of any small regulatory proteins associated with the H,K-ATPase.
Figures



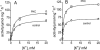
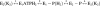

References
-
- Asahi, M., Y. Kimura, K. Kurzydlowski, M. Tada, and D. H. MacLennan. 1999. Transmembrane helix M6 in Sarco(endo)plasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase forms a functional site with phospholamban. Evidence for a physical interaction at other sites. J. Biol. Chem. 274:32855–32862. - PubMed
-
- Baginski, E. S., P. P. Foa, and B. Zak. 1967. Determination of phosphate: study of labile organic phosphate interference. Clin. Chim. Acta. 14:155–158.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

