Effects of epicholesterol on the phosphatidylcholine bilayer: a molecular simulation study
- PMID: 12609883
- PMCID: PMC1302750
- DOI: 10.1016/S0006-3495(03)74989-3
Effects of epicholesterol on the phosphatidylcholine bilayer: a molecular simulation study
Abstract
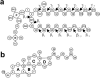
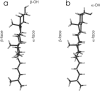
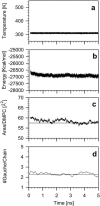
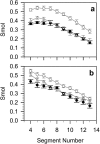
Epicholesterol (Echol) is an epimeric form of cholesterol (Chol). A molecular dynamics simulation of the fully hydrated dimyristoylphosphatidylcholine-Echol (DMPC-Echol) bilayer membrane containing approximately 22 mol % of Echol was carried out for 5 ns. A 3-ns trajectory generated between 2 and 5 ns of molecular dynamics simulation was used for analyses to determine the effects of Echol on the membrane properties. As reference systems, pure DMPC and mixed DMPC-Chol bilayers were used. The study shows that Echol, like Chol, changes the organization of the bilayer/water interface and increases membrane order and condensation, but to a lesser degree. Effects of both sterols are based on the same atomic level mechanisms; their different strength arises from different vertical localizations of Echol and Chol hydroxyl groups in the membrane/water interface.
Figures




References
-
- Berendsen, H. J. C., J. P. M. Postma, W. F. van Gunsteren, A. DiNola, and J. R. Haak. 1984. Molecular dynamics with coupling to an external bath. J. Chem. Phys. 81:3684–3690.
-
- Brainard, J. R., and E. H. Cordes. 1981. Carbon-13 nuclear magnetic resonance studies of cholesterol-egg yolk phosphatidylcholine vesicles. Biochemistry. 20:4607–4617. - PubMed
-
- Brzozowska, I., and Z. A. Figaszewski. 2002. The equilibrium of phosphatidylcholine-cholesterol in monolayers at the air/water interface. Colloid Surface B. 23:51–58.
-
- Charifson, P. S., R. G. Hiskey, and L. G. Pedersen. 1990. Construction and molecular modeling of phospholipid surfaces. J. Comp. Chem. 11:1181–1186.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

