Computer simulations of membrane protein folding: structure and dynamics
- PMID: 12609892
- PMCID: PMC1302759
- DOI: 10.1016/S0006-3495(03)74998-4
Computer simulations of membrane protein folding: structure and dynamics
Abstract
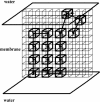
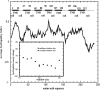
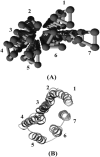
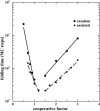
A lattice model of membrane proteins with a composite energy function is proposed to study their folding dynamics and native structures using Monte Carlo simulations. This model successfully predicts the seven helix bundle structure of sensory rhodopsin I by practicing a three-stage folding. Folding dynamics of a transmembrane segment into a helix is further investigated by varying the cooperativity in the formation of alpha helices for both random folding and assisted folding. The chain length dependence of the folding time of a hydrophobic segment to a helical state is studied for both free and anchored chains. An unusual length dependence in the folding time of anchored chains is observed.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Deciphering the folding kinetics of transmembrane helical proteins.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000 Dec 19;97(26):14229-34. doi: 10.1073/pnas.97.26.14229. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000. PMID: 11121029 Free PMC article.
-
Entropy reduction effect imposed by hydrogen bond formation on protein folding cooperativity: evidence from a hydrophobic minimalist model.Phys Rev E Stat Nonlin Soft Matter Phys. 2005 Nov;72(5 Pt 1):051903. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.72.051903. Epub 2005 Nov 1. Phys Rev E Stat Nonlin Soft Matter Phys. 2005. PMID: 16383641
-
Comparison of stability predictions and simulated unfolding of rhodopsin structures.Photochem Photobiol. 2007 Mar-Apr;83(2):351-62. doi: 10.1562/2006-06-20-RA-942. Photochem Photobiol. 2007. PMID: 17576347
-
A successful change of circumstance: a transition state for membrane protein folding.Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2012 Aug;22(4):469-75. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2012.03.008. Epub 2012 Apr 2. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2012. PMID: 22475521 Review.
-
Dynamic Monte Carlo simulations of a new lattice model of globular protein folding, structure and dynamics.J Mol Biol. 1991 Sep 20;221(2):499-531. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)80070-b. J Mol Biol. 1991. PMID: 1920430 Review.
Cited by
-
Conformational temperature-dependent behavior of a histone H2AX: a coarse-grained Monte Carlo approach via knowledge-based interaction potentials.PLoS One. 2012;7(3):e32075. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0032075. Epub 2012 Mar 19. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22442661 Free PMC article.
-
Contact-induced structure transformation in transmembrane prion propagation.Biophys J. 2007 Apr 15;92(8):2704-10. doi: 10.1529/biophysj.106.098335. Epub 2007 Jan 26. Biophys J. 2007. PMID: 17259269 Free PMC article.
-
Computational prediction of kink properties of helices in membrane proteins.J Comput Aided Mol Des. 2014 Feb;28(2):99-109. doi: 10.1007/s10822-014-9734-2. Epub 2014 Feb 21. J Comput Aided Mol Des. 2014. PMID: 24557854
-
Viral channel forming proteins--How to assemble and depolarize lipid membranes in silico.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016 Jul;1858(7 Pt B):1710-21. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2016.01.018. Epub 2016 Jan 22. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016. PMID: 26806161 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Replica exchange Monte-Carlo simulations of helix bundle membrane proteins: rotational parameters of helices.J Comput Aided Mol Des. 2012 Mar;26(3):363-74. doi: 10.1007/s10822-012-9562-1. Epub 2012 Mar 31. J Comput Aided Mol Des. 2012. PMID: 22466784
References
-
- Arumugam, S., S. Pascal, C. L. North, W. Hu, K. C. Lee, M. Cotten, R. R. Ketchem, F. Xu, M. Brenneman, F. Kovacs, F. Tian, A. Wang, S. Huo, and T. A. Cross. 1996. Conformational trapping in a membrane environment: a regulatory mechanism for protein activity? Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 93:5872–5876. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bryngelson, J. D., and P. G. Wolynes. 1989. Intermediates and barrier crossing in a random energy model (with applications to protein folding). J. Phys. Chem. 93:6902–6915.
-
- Cantor, C. R., and P. R. Schimmel. 1980. Biophysical Chemistry. W. H. Freeman Company, San Francisco. 862–863.
-
- Carmesin, I., and K. Kremer. 1988. The bond fluctuation method: a new effective algorithm for the dynamics of polymers in all spatial dimensions. Macromolecules. 21:2819–2823.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

