Role of hydrophobic clusters and long-range contact networks in the folding of (alpha/beta)8 barrel proteins
- PMID: 12609894
- PMCID: PMC1302761
- DOI: 10.1016/s0006-3495(03)75000-0
Role of hydrophobic clusters and long-range contact networks in the folding of (alpha/beta)8 barrel proteins
Abstract
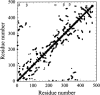
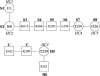
Analysis on the three dimensional structures of (alpha/beta)(8) barrel proteins provides ample light to understand the factors that are responsible for directing and maintaining their common fold. In this work, the hydrophobically enriched clusters are identified in 92% of the considered (alpha/beta)(8) barrel proteins. The residue segments with hydrophobic clusters have high thermal stability. Further, these clusters are formed and stabilized through long-range interactions. Specifically, a network of long-range contacts connects adjacent beta-strands of the (alpha/beta)(8) barrel domain and the hydrophobic clusters. The implications of hydrophobic clusters and long-range networks in providing a feasible common mechanism for the folding of (alpha/beta)(8) barrel proteins are proposed.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Role of long- and short-range hydrophobic, hydrophilic and charged residues contact network in protein's structural organization.BMC Bioinformatics. 2012 Jun 21;13:142. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-13-142. BMC Bioinformatics. 2012. PMID: 22720789 Free PMC article.
-
Importance of long-range interactions in (alpha/beta)8 barrel fold.J Protein Chem. 1998 Oct;17(7):691-7. doi: 10.1007/BF02780972. J Protein Chem. 1998. PMID: 9853685
-
An analysis of the amino acid clustering pattern in (alpha/beta)8 barrel proteins.J Protein Chem. 1998 Jul;17(5):407-15. doi: 10.1023/a:1022514400583. J Protein Chem. 1998. PMID: 9717737
-
Folding by numbers: primary sequence statistics and their use in studying protein folding.Int J Mol Sci. 2009 Apr 8;10(4):1567-1589. doi: 10.3390/ijms10041567. Int J Mol Sci. 2009. PMID: 19468326 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The up-and-down beta-barrel proteins.FASEB J. 1994 Dec;8(15):1240-7. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.8.15.8001736. FASEB J. 1994. PMID: 8001736 Review.
Cited by
-
De Novo Design of a Highly Stable Ovoid TIM Barrel: Unlocking Pocket Shape towards Functional Design.Biodes Res. 2022 Oct 10;2022:9842315. doi: 10.34133/2022/9842315. eCollection 2022. Biodes Res. 2022. PMID: 37850141 Free PMC article.
-
Prediction of inter-residue contact clusters from hydrophobic cores.Int J Data Min Bioinform. 2008 Dec 11;2008:703-708. doi: 10.1109/ICMLA.2008.74. Int J Data Min Bioinform. 2008. PMID: 20802820 Free PMC article.
-
Role of long- and short-range hydrophobic, hydrophilic and charged residues contact network in protein's structural organization.BMC Bioinformatics. 2012 Jun 21;13:142. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-13-142. BMC Bioinformatics. 2012. PMID: 22720789 Free PMC article.
-
Network Connectivity, Centrality and Fragmentation in the Greek-Key Protein Topology.Protein J. 2019 Oct;38(5):497-505. doi: 10.1007/s10930-019-09850-7. Protein J. 2019. PMID: 31317305
-
Specific non-local interactions are not necessary for recovering native protein dynamics.PLoS One. 2014 Mar 13;9(3):e91347. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0091347. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24625758 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chothia, C. 1988. Protein structure: the 14th barrel rolls out. Nature. 333:598–599. - PubMed
-
- Debe, D. A., and W. A. Goddard. 1999. First principles prediction of protein folding rates. J. Mol. Biol. 294:619–625. - PubMed
-
- Dobson, C. M., and M. Karplus. 1999. The fundamentals of protein folding: bringing together theory and experiment. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 9:92–101. - PubMed
-
- Dosztanyi, Z., A. Fiser, and I. Simon. 1997. Stabilization centers in proteins: identification, characterization and predictions. J. Mol. Biol. 272:597–612. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

