The position of QB in the photosynthetic reaction center depends on pH: a theoretical analysis of the proton uptake upon QB reduction
- PMID: 12609910
- PMCID: PMC1302777
- DOI: 10.1016/S0006-3495(03)75016-4
The position of QB in the photosynthetic reaction center depends on pH: a theoretical analysis of the proton uptake upon QB reduction
Abstract
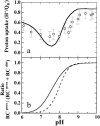
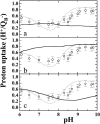
Electrostatics-based calculations have been performed to examine the proton uptake upon reduction of the terminal electron acceptor Q(B) in the photosynthetic reaction center of Rhodobacter sphaeroides as a function of pH and the associated conformational equilibrium. Two crystal structures of the reaction center were considered: one structure was determined in the dark and the other under illumination. In the two structures, the Q(B) was found in two different positions, proximal or distal to the nonheme iron. Because Q(B) was found mainly in the distal position in the dark and only in the proximal position under illumination, the two positions have been attributed mostly to the oxidized and the reduced forms of Q(B), respectively. We calculated the proton uptake upon Q(B) reduction by four different models. In the first model, Q(B) is allowed to equilibrate between the two positions with either oxidation state. This equilibrium was allowed to vary with pH. In the other three models the distribution of Q(B) between the proximal position and the distal position was pH-independent, with Q(B) occupying only the distal position or only the proximal position or populating the two positions with a fixed ratio. Only the first model, which includes the pH-dependent conformational equilibrium, reproduces both the experimentally measured pH dependence of the proton uptake and the crystallographically observed conformational equilibrium at pH 8. From this model, we find that Q(B) occupies only the distal position below pH 6.5 and only the proximal position above pH 9.0 in both oxidation states. Between these pH values both positions are partially occupied. The reduced Q(B) has a higher occupancy in the proximal position than the oxidized Q(B). In summary, the present results indicate that the conformational equilibrium of Q(B) depends not only on the redox state of Q(B), but also on the pH value of the solution.
Figures



Similar articles
-
pH modulates the quinone position in the photosynthetic reaction center from Rhodobacter sphaeroides in the neutral and charge separated states.J Mol Biol. 2007 Aug 10;371(2):396-409. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2007.04.082. Epub 2007 May 10. J Mol Biol. 2007. PMID: 17570397
-
Coupling of electron transfer to proton uptake at the Q(B) site of the bacterial reaction center: a perspective from FTIR difference spectroscopy.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2008 Oct;1777(10):1229-48. doi: 10.1016/j.bbabio.2008.06.012. Epub 2008 Jul 11. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2008. PMID: 18671937 Review.
-
Calculated protein and proton motions coupled to electron transfer: electron transfer from QA- to QB in bacterial photosynthetic reaction centers.Biochemistry. 1999 Jun 29;38(26):8253-70. doi: 10.1021/bi982700a. Biochemistry. 1999. PMID: 10387071
-
Reduction and protonation of the secondary quinone acceptor of Rhodobacter sphaeroides photosynthetic reaction center: kinetic model based on a comparison of wild-type chromatophores with mutants carrying Arg-->Ile substitution at sites 207 and 217 in the L-subunit.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2000 Jul 20;1459(1):10-34. doi: 10.1016/s0005-2728(00)00110-9. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2000. PMID: 10924896
-
Proton and electron transfer in bacterial reaction centers.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2000 May 12;1458(1):148-63. doi: 10.1016/s0005-2728(00)00065-7. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2000. PMID: 10812030 Review.
Cited by
-
Investigating the mechanisms of photosynthetic proteins using continuum electrostatics.Photosynth Res. 2008 Jul;97(1):33-53. doi: 10.1007/s11120-008-9306-1. Epub 2008 May 14. Photosynth Res. 2008. PMID: 18478354 Review.
-
Time-resolved crystallographic studies of light-induced structural changes in the photosynthetic reaction center.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004 Apr 20;101(16):5982-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0306840101. Epub 2004 Apr 8. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004. PMID: 15073325 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alexov, E., J. Miksovska, L. Baciou, M. Schiffer, D. K. Hanson, P. Sebban, and M. R. Gunner. 2000. Modeling the effects of mutations on the free energy of the first electron transfer from QA− to QB in photosynthetic reaction centers. Biochemistry. 39:5940–5952. - PubMed
-
- Alexov, E. G., and M. R. Gunner. 1999. Calculated protein and proton motions coupled to electron transfer: electron transfer from QA− to QB in bacterial photosynthetic reaction centers. Biochemistry. 38:8253–8270. - PubMed
-
- Allen, J. 1994. Crystallization of the reaction center from Rhodobacter sphaeroides in a new tetragonal form. Proteins. 20:283–286. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

