The STAT2 activation process is a crucial target of Sendai virus C protein for the blockade of alpha interferon signaling
- PMID: 12610111
- PMCID: PMC149518
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.77.6.3360-3370.2003
The STAT2 activation process is a crucial target of Sendai virus C protein for the blockade of alpha interferon signaling
Abstract
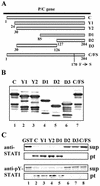
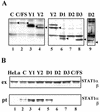
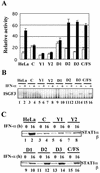
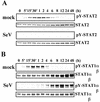
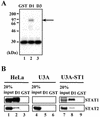
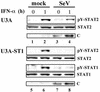
Sendai virus (SeV) C protein functions as an interferon (IFN) antagonist and renders cells unresponsive to both alpha/beta IFN (IFN-alpha/beta) and IFN-gamma. We have recently found the physical association of the C protein with signal transducer and activator of transcription 1 (STAT1) in infected cells. However, involvement of the C-STAT1 interaction in the blockade of IFN signaling has remained unclear. We generated here a series of C mutant proteins that retained or lost the STAT1-binding capacity and examined their effects on IFN-alpha signaling. All of the C mutant proteins with no STAT1-binding capacity lost the ability to inhibit the IFN-alpha response. In contrast, the C mutant proteins retaining the STAT1-binding capacity suppressed IFN-alpha-stimulated tyrosine phosphorylation of both STAT2 and STAT1 to various degrees. Remarkably, their anti-IFN-alpha capacities correlated well with the inhibitory effect on phosphorylation of STAT2 rather than STAT1. In infected cells, the levels of tyrosine-phosphorylated (pY) STAT2 were below the detection level irrespective of duration of IFN-alpha stimulation, whereas the levels of pY-STAT1 strikingly increased after long-term IFN-alpha stimulation. These results suggest that the STAT2 activation process is a crucial target for the blockade of IFN-alpha signaling. An in vitro binding assay with extracts from (STAT1-deficient) U3A and (STAT1-expressing) U3A-ST1 cells suggested the requirement of STAT1 for the C-STAT2 interaction. Furthermore, expression of STAT1 enhanced the inhibitory effect of the C protein on STAT2 activation in U3A cells. The C protein thus appears to participate in the inhibitory process for STAT2 activation through the STAT1 interaction.
Figures


References
-
- Andrejeva, J., D. F. Young, S. Goodbourn, and R. E. Randall. 2002. Degradation of STAT1 and STAT2 by the V proteins of simian virus 5 and human parainfluenza virus type 2, respectively: consequences for virus replication in the presence of alpha/beta and gamma interferons. J. Virol. 76:2159-2167. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Asao, H., and X. Y. Fu. 2000. Interferon-gamma has dual potentials in inhibiting or promoting cell proliferation. J. Biol. Chem. 275:867-874. - PubMed
-
- Chatziandreou, N., D. Young, J. Andrejeva, S. Goodbourn, and R. E. Randall. 2002. Differences in interferon sensitivity and biological properties of two related isolates of simian virus 5: a model for virus persistence. Virology 293:234-242. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

