The human cytomegalovirus major immediate-early enhancer determines the efficiency of immediate-early gene transcription and viral replication in permissive cells at low multiplicity of infection
- PMID: 12610136
- PMCID: PMC149520
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.77.6.3602-3614.2003
The human cytomegalovirus major immediate-early enhancer determines the efficiency of immediate-early gene transcription and viral replication in permissive cells at low multiplicity of infection
Abstract
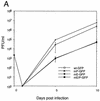
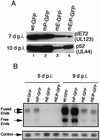
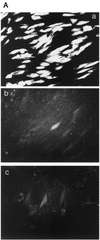
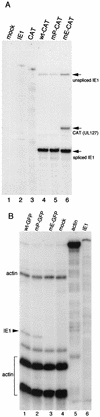
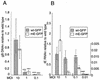
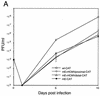
To determine the effect of the human cytomegalovirus (CMV) major immediate-early (MIE) enhancer or promoter on the efficiency of viral replication in permissive human cells, we constructed recombinant viruses with their human MIE promoter, enhancer, and promoter plus enhancer replaced with the murine CMV components. After a low multiplicity of infection (MOI) (0.01 PFU/cell), recombinant human CMV with the murine CMV promoter replicated like the wild type but recombinant virus with the murine enhancer replicated less efficiently. Immediate-early (IE) viral protein pIE72 (UL123), early viral protein (UL44), and viral DNA synthesis were significantly decreased. The effect of the human CMV enhancer substitution with the murine CMV enhancer was also demonstrated in different cell types by using recombinant virus with the UL127 promoter, driving the expression of green fluorescent protein (GFP). After an MOI of 1, GFP expression was high with the human CMV enhancer and significantly lower with the murine CMV enhancer. Even though at a high MOI (10 PFU/cell), the murine CMV enhancer was as efficient as the human CMV enhancer for the transcription of IE genes in human foreskin fibroblast cells, at lower MOIs, the murine CMV enhancer was less efficient. Proximal and distal chimeras of the human and murine enhancers also replicated less efficiently at a low MOI and expressed lower levels of GFP from the UL127 promoter. These experiments demonstrate that the entire human CMV enhancer has evolved for the efficient expression of the viral IE and early genes in human cells. Possible functions of the human CMV enhancer and promoter at a low MOI are discussed.
Figures






Similar articles
-
The human cytomegalovirus major immediate-early distal enhancer region is required for efficient viral replication and immediate-early gene expression.J Virol. 2000 Feb;74(4):1602-13. doi: 10.1128/jvi.74.4.1602-1613.2000. J Virol. 2000. PMID: 10644329 Free PMC article.
-
A strong negative transcriptional regulatory region between the human cytomegalovirus UL127 gene and the major immediate-early enhancer.J Virol. 1999 Nov;73(11):9039-52. doi: 10.1128/JVI.73.11.9039-9052.1999. J Virol. 1999. PMID: 10516010 Free PMC article.
-
Role of the cytomegalovirus major immediate early enhancer in acute infection and reactivation from latency.Med Microbiol Immunol. 2008 Jun;197(2):223-31. doi: 10.1007/s00430-007-0069-7. Epub 2007 Dec 19. Med Microbiol Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18097687 Review.
-
Role of the proximal enhancer of the major immediate-early promoter in human cytomegalovirus replication.J Virol. 2004 Dec;78(23):12788-99. doi: 10.1128/JVI.78.23.12788-12799.2004. J Virol. 2004. PMID: 15542631 Free PMC article.
-
Coordination of late gene transcription of human cytomegalovirus with viral DNA synthesis: recombinant viruses as potential therapeutic vaccine candidates.Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2013 Feb;17(2):157-66. doi: 10.1517/14728222.2013.740460. Epub 2012 Dec 12. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2013. PMID: 23231449 Review.
Cited by
-
Novel Enhanced Mammalian Cell Transient Expression Vector via Promoter Combination.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Feb 16;25(4):2330. doi: 10.3390/ijms25042330. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38397006 Free PMC article.
-
Specific RNA structures in the 5' untranslated region of the human cytomegalovirus major immediate early transcript are critical for efficient virus replication.mBio. 2024 Feb 14;15(2):e0262123. doi: 10.1128/mbio.02621-23. Epub 2024 Jan 2. mBio. 2024. PMID: 38165154 Free PMC article.
-
Murine cytomegalovirus major immediate-early enhancer region operating as a genetic switch in bidirectional gene pair transcription.J Virol. 2007 Jul;81(14):7805-10. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02388-06. Epub 2007 May 9. J Virol. 2007. PMID: 17494084 Free PMC article.
-
Human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived models to investigate human cytomegalovirus infection in neural cells.PLoS One. 2012;7(11):e49700. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0049700. Epub 2012 Nov 27. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23209593 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence of human cytomegalovirus, polyomaviruses, and oncogenic viruses in glioblastoma among Japanese subjects.Infect Agent Cancer. 2015 Jan 27;10:3. doi: 10.1186/1750-9378-10-3. eCollection 2015. Infect Agent Cancer. 2015. PMID: 25685179 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anders, D. G., and L. A. McCue. 1996. The human cytomegalovirus genes and proteins required for DNA synthesis. Intervirology 39:378-388. - PubMed
-
- Angulo, A., C. Suto, R. A. Heyman, and P. Ghazal. 1995. Characterization of the sequences of the human cytomegalovirus enhancer that mediate differential regulation by natural and synthetic retinoids. Mol. Endocrinol. 10:781-793. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

