In vitro selection and characterization of hepatitis C virus serine protease variants resistant to an active-site peptide inhibitor
- PMID: 12610142
- PMCID: PMC149541
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.77.6.3669-3679.2003
In vitro selection and characterization of hepatitis C virus serine protease variants resistant to an active-site peptide inhibitor
Abstract
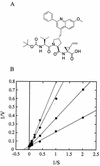
The hepatitis C virus (HCV) serine protease is necessary for viral replication and represents a valid target for developing new therapies for HCV infection. Potent and selective inhibitors of this enzyme have been identified and shown to inhibit HCV replication in tissue culture. The optimization of these inhibitors for clinical development would greatly benefit from in vitro systems for the identification and the study of resistant variants. We report the use HCV subgenomic replicons to isolate and characterize mutants resistant to a protease inhibitor. Taking advantage of the replicons' ability to transduce resistance to neomycin, we selected replicons with decreased sensitivity to the inhibitor by culturing the host cells in the presence of the inhibitor and neomycin. The selected replicons replicated to the same extent as those in parental cells. Sequence analysis followed by transfection of replicons containing isolated mutations revealed that resistance was mediated by amino acid substitutions in the protease. These results were confirmed by in vitro experiments with mutant enzymes and by modeling the inhibitor in the three-dimensional structure of the protease.
Figures


Comment in
-
Evasive maneuvers by hepatitis C virus.Hepatology. 2003 Sep;38(3):769-71. doi: 10.1002/hep.510380327. Hepatology. 2003. PMID: 12939603
References
-
- Barbato, G., D. O. Cicero, M. C. Nardi, C. Steinkuhler, R. Cortese, R. De Francesco, and R. Bazzo. 1999. The solution structure of the N-terminal proteinase domain of the hepatitis C virus (HCV) NS3 protein provides new insights into its activation and catalytic mechanism. J. Mol. Biol. 289:371-384. - PubMed
-
- Bartenschlager, R. 1997. Candidate targets for hepatitis C virus-specific antiviral therapy. Intervirology 40:378-393. - PubMed
-
- Bartenschlager, R. 1999. The NS3/4A proteinase of the hepatitis C virus: unravelling structure and function of an unusual enzyme and a prime target for antiviral therapy. J. Viral Hepat. 6:165-181. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

