Transmembrane domains 1 and 2 of the latent membrane protein 1 of Epstein-Barr virus contain a lipid raft targeting signal and play a critical role in cytostasis
- PMID: 12610149
- PMCID: PMC149527
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.77.6.3749-3758.2003
Transmembrane domains 1 and 2 of the latent membrane protein 1 of Epstein-Barr virus contain a lipid raft targeting signal and play a critical role in cytostasis
Abstract
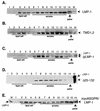
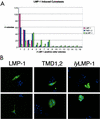
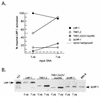
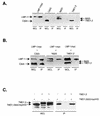
The latent membrane protein 1 (LMP-1) oncoprotein of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) is a constitutively active, CD40-like cell surface signaling protein essential for EBV-mediated human B-cell immortalization. Like ligand-activated CD40, LMP-1 activates NF-kappaB and Jun kinase signaling pathways via binding, as a constitutive oligomer, to tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factors (TRAFs). LMP-1's lipid raft association and oligomerization have been linked to its activation of cell signaling pathways. Both oligomerization and lipid raft association require the function of LMP-1's polytopic multispanning transmembrane domain, a domain that is indispensable for LMP-1's growth-regulatory signaling activities. We have begun to address the sequence requirements of the polytopic hydrophobic transmembrane domain for LMP-1's signaling and biochemical activities. Here we report that transmembrane domains 1 and 2 are sufficient for LMP-1's lipid raft association and cytostatic activity. Transmembrane domains 1 and 2 support NF-kappaB activation, albeit less potently than does the entire polytopic transmembrane domain. Interestingly, LMP-1's first two transmembrane domains are not sufficient for oligomerization or TRAF binding. These results suggest that lipid raft association and oligomerization are mediated by distinct and separable activities of LMP-1's polytopic transmembrane domain. Additionally, lipid raft association, mediated by transmembrane domains 1 and 2, plays a significant role in LMP-1 activation, and LMP-1 can activate NF-kappaB via an oligomerization/TRAF binding-independent mechanism. To our knowledge, this is the first demonstration of an activity's being linked to individual membrane-spanning domains within LMP-1's polytopic transmembrane domain.
Figures

Similar articles
-
LMP-1's transmembrane domains encode multiple functions required for LMP-1's efficient signaling.J Virol. 2002 Nov;76(22):11551-60. doi: 10.1128/jvi.76.22.11551-11560.2002. J Virol. 2002. PMID: 12388716 Free PMC article.
-
The cytoplasmic amino-terminus of the Latent Membrane Protein-1 of Epstein-Barr Virus: relationship between transmembrane orientation and effector functions of the carboxy-terminus and transmembrane domain.Oncogene. 2001 Aug 30;20(38):5313-30. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1204689. Oncogene. 2001. PMID: 11536044
-
High molecular weight complex analysis of Epstein-Barr virus Latent Membrane Protein 1 (LMP-1): structural insights into LMP-1's homo-oligomerization and lipid raft association.Virus Res. 2013 Dec 26;178(2):314-27. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2013.09.025. Epub 2013 Sep 25. Virus Res. 2013. PMID: 24075898 Free PMC article.
-
LMP1 TRAFficking activates growth and survival pathways.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2007;597:173-87. doi: 10.1007/978-0-387-70630-6_14. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2007. PMID: 17633026 Review.
-
The Latent Membrane Protein 1 (LMP1).Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2015;391:119-49. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-22834-1_4. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2015. PMID: 26428373 Review.
Cited by
-
Transmembrane Domains Mediate Intra- and Extracellular Trafficking of Epstein-Barr Virus Latent Membrane Protein 1.J Virol. 2018 Aug 16;92(17):e00280-18. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00280-18. Print 2018 Sep 1. J Virol. 2018. PMID: 29950415 Free PMC article.
-
Cross-regulation between herpesviruses and the TNF superfamily members.Nat Rev Immunol. 2008 Nov;8(11):861-73. doi: 10.1038/nri2434. Nat Rev Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18949019 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epstein-barr virus latent membrane protein 2B (LMP2B) modulates LMP2A activity.J Virol. 2007 Jan;81(1):84-94. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01302-06. Epub 2006 Oct 11. J Virol. 2007. PMID: 17035319 Free PMC article.
-
PRA1 promotes the intracellular trafficking and NF-kappaB signaling of EBV latent membrane protein 1.EMBO J. 2006 Sep 6;25(17):4120-30. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601282. Epub 2006 Aug 17. EMBO J. 2006. PMID: 16917502 Free PMC article.
-
Lanthanide-Based Peptide-Directed Visible/Near-Infrared Imaging and Inhibition of LMP1.JACS Au. 2021 Jun 20;1(7):1034-1043. doi: 10.1021/jacsau.1c00187. eCollection 2021 Jul 26. JACS Au. 2021. PMID: 34467347 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baer, R., A. T. Bankier, M. D. Biggin, P. L. Deininger, P. J. Farrell, T. J. Gibson, G. Hatfull, G. S. Hudson, S. C. Satchwell, C. Seguin, et al. 1984. DNA sequence and expression of the B95-8 Epstein-Barr virus genome. Nature 310:207-211. - PubMed
-
- Clausse, B., K. Fizazi, V. Walczak, C. Tetaud, J. Wiels, T. Tursz, and P. Busson. 1997. High concentration of the EBV latent membrane protein 1 in glycosphingolipid-rich complexes from both epithelial and lymphoid cells. Virology 228:285-293. - PubMed
-
- Coffin, W. F., III, K. D. Erickson, M. Hoedt-Miller, and J. M. Martin. 2001. The cytoplasmic amino-terminus of the latent membrane protein-1 of Epstein-Barr virus: relationship between transmembrane orientation and effector functions of the carboxy-terminus. Oncogene 20:5313-5330. - PubMed
-
- DiMaio, D., C. Lai, and D. Mattoon. 2000. The platelet-derived growth factor B receptor as a target of the bovine papillomavirus E5 protein. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 11:283-293. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

