Acute hypoxia occludes hTREK-1 modulation: re-evaluation of the potential role of tandem P domain K+ channels in central neuroprotection
- PMID: 12611912
- PMCID: PMC2342782
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2003.040048
Acute hypoxia occludes hTREK-1 modulation: re-evaluation of the potential role of tandem P domain K+ channels in central neuroprotection
Abstract
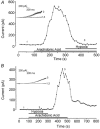
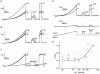
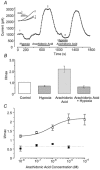
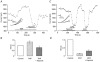
The human tandem P domain K+ channel hTREK-1 (KCNK2) is distributed widely through the CNS. Here, whole-cell patch clamp recordings were employed to investigate the effects of hypoxia on hTREK-1 channels stably expressed in human embryonic kidney cells. Acute hypoxia caused a rapid and reversible inhibition of whole-cell K+ current amplitudes; this was PO2 dependent with a maximal inhibition achieved at 60 mmHg and below. In accordance with previous studies, hTREK-1 current amplitudes were enhanced by arachidonic acid. This effect was concentration dependent, with maximal enhancement observed at a concentration of 10 microM. Membrane deformation by the crenator trinitrophenol (to mimic cell swelling) or the cup former chlorpromazine (to mimic cell shrinkage) caused robust activation and inhibition of currents, respectively. However, current augmentation by either arachidonic acid or trinitrophenol was completely prevented during hypoxia; conversely, hypoxia blunted the inhibitory action of chlorpromazine. The abilities of arachidonic acid to augment currents and of hypoxia to completely abrogate this effect were also observed in cell-attached patches. Our data indicate that hypoxia interacts with hTREK-1, and occludes its modulation by arachidonic acid and membrane deformation. These findings also suggest that the potential neuroprotective role of TREK channels, which has recently been proposed, requires reconsideration since hTREK-1 activation is unlikely when ambient PO2 is below 60 mmHg - a situation which normally pertains in the CNS even during systemic normoxia.
Figures
References
-
- Bang H, Kim Y, Kim D. TREK-2, a new member of the mechanosensitive tandem-pore K+ channel family. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:17412–17419. - PubMed
-
- Duprat F, Lesage F, Patel AJ, Fink M, Romey G, Lazdunski M. The neuroprotective agent riluzole activates the two P domain K+ channels TREK-1 and TRAAK. Mol Pharmacol. 2000;57:906–912. - PubMed
-
- Fearon IM, Varadi G, Koch S, Isaacsohn I, Ball SG, Peers C. Splice variants reveal the region involved in oxygen sensing by recombinant human L-type Ca2+ channels. Circ Res. 2000;87:537–539. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

