Human transcription elongation factor NELF: identification of novel subunits and reconstitution of the functionally active complex
- PMID: 12612062
- PMCID: PMC149481
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.23.6.1863-1873.2003
Human transcription elongation factor NELF: identification of novel subunits and reconstitution of the functionally active complex
Abstract
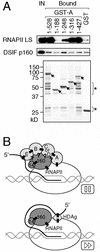
The multisubunit transcription elongation factor NELF (for negative elongation factor) acts together with DRB (5,6-dichloro-1-beta-D-ribofuranosylbenzimidazole) sensitivity-inducing factor (DSIF)/human Spt4-Spt5 to cause transcriptional pausing of RNA polymerase II (RNAPII). NELF activity is associated with five polypeptides, A to E. NELF-A has sequence similarity to hepatitis delta antigen (HDAg), the viral protein that binds to and activates RNAPII, whereas NELF-E is an RNA-binding protein whose RNA-binding activity is critical for NELF function. To understand the interactions of DSIF, NELF, and RNAPII at a molecular level, we identified the B, C, and D proteins of human NELF. NELF-B is identical to COBRA1, recently reported to associate with the product of breast cancer susceptibility gene BRCA1. NELF-C and NELF-D are highly related or identical to the protein called TH1, of unknown function. NELF-B and NELF-C or NELF-D are integral subunits that bring NELF-A and NELF-E together, and coexpression of these four proteins in insect cells resulted in the reconstitution of functionally active NELF. Detailed analyses using mutated recombinant complexes indicated that the small region of NELF-A with similarity to HDAg is critical for RNAPII binding and for transcriptional pausing. This study defines several important protein-protein interactions and opens the way for understanding the mechanism of DSIF- and NELF-induced transcriptional pausing.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Interactions between DSIF (DRB sensitivity inducing factor), NELF (negative elongation factor), and the Drosophila RNA polymerase II transcription elongation complex.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010 Jun 22;107(25):11301-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1000681107. Epub 2010 Jun 4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010. PMID: 20534440 Free PMC article.
-
Evidence that negative elongation factor represses transcription elongation through binding to a DRB sensitivity-inducing factor/RNA polymerase II complex and RNA.Mol Cell Biol. 2002 May;22(9):2918-27. doi: 10.1128/MCB.22.9.2918-2927.2002. Mol Cell Biol. 2002. PMID: 11940650 Free PMC article.
-
DSIF and NELF interact with RNA polymerase II elongation complex and HIV-1 Tat stimulates P-TEFb-mediated phosphorylation of RNA polymerase II and DSIF during transcription elongation.J Biol Chem. 2001 Apr 20;276(16):12951-8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M006130200. Epub 2000 Dec 8. J Biol Chem. 2001. PMID: 11112772
-
Transcription elongation factors DSIF and NELF: promoter-proximal pausing and beyond.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 Jan;1829(1):98-104. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2012.11.007. Epub 2012 Nov 29. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013. PMID: 23202475 Review.
-
HIV-1 Tat: coping with negative elongation factors.Curr Opin Immunol. 1999 Aug;11(4):460-5. doi: 10.1016/S0952-7915(99)80077-6. Curr Opin Immunol. 1999. PMID: 10448148 Review.
Cited by
-
Enhancer RNAs stimulate Pol II pause release by harnessing multivalent interactions to NELF.Nat Commun. 2022 May 4;13(1):2429. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-29934-w. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 35508485 Free PMC article.
-
Overexpression of NELFCD promotes colorectal cancer cells proliferation, migration, and invasion.Onco Targets Ther. 2018 Dec 5;11:8741-8750. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S186266. eCollection 2018. Onco Targets Ther. 2018. PMID: 30584332 Free PMC article.
-
Cofactor of BRCA1 modulates androgen-dependent transcription and alternative splicing.J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2007 Nov-Dec;107(3-5):131-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2007.05.031. Epub 2007 Jun 27. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2007. PMID: 17659869 Free PMC article.
-
Interactions between DSIF (DRB sensitivity inducing factor), NELF (negative elongation factor), and the Drosophila RNA polymerase II transcription elongation complex.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010 Jun 22;107(25):11301-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1000681107. Epub 2010 Jun 4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010. PMID: 20534440 Free PMC article.
-
Origin of RNA Polymerase II pause in eumetazoans: Insights from Hydra.J Biosci. 2020;45:8. doi: 10.1007/s12038-019-9979-y. J Biosci. 2020. PMID: 31965986 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bonthron, D. T., B. E. Hayward, V. Moran, and L. Strain. 2000. Characterization of TH1 and CTSZ, two non-imprinted genes downstream of GNAS1 in chromosome 20q13. Hum. Genet. 107:165-175. - PubMed
-
- Chao, S. H., K. Fujinaga, J. E. Marion, R. Taube, E. A. Sausville, A. M. Senderowicz, B. M. Peterlin, and D. H. Price. 2000. Flavopiridol inhibits P-TEFb and blocks HIV-1 replication. J. Biol. Chem. 275:28345-28348. - PubMed
-
- Garber, M. E., and K. A. Jones. 1999. HIV-1 Tat: coping with negative elongation factors. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 11:460-465. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
