RNA polymerase II accumulation in the promoter-proximal region of the dihydrofolate reductase and gamma-actin genes
- PMID: 12612070
- PMCID: PMC149466
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.23.6.1961-1967.2003
RNA polymerase II accumulation in the promoter-proximal region of the dihydrofolate reductase and gamma-actin genes
Abstract
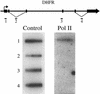
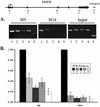
The carboxyl-terminal domain (CTD) of RNA polymerase II (Pol II) can be phosphorylated at serine 2 (Ser-2) and serine 5 (Ser-5) of the CTD heptad repeat YSPTSPS, and this phosphorylation is important in coupling transcription to RNA processing, including 5' capping, splicing, and polyadenylation. The mammalian endogenous dihydrofolate reductase and gamma-actin genes have been used to study the association of Pol II with different regions of transcribed genes (promoter-proximal compared to distal regions) and the phosphorylation status of its CTD. For both genes, Pol II is more concentrated in the promoter-proximal regions than in the interior regions. Moreover, different phosphorylation forms of Pol II are associated with distinct regions. Ser-5 phosphorylation of Pol II is concentrated near the promoter, while Ser-2 phosphorylation is observed throughout the gene. These results suggest that the accumulation of paused Pol II in promoter-proximal regions may be a common feature of gene regulation in mammalian cells.
Figures




References
-
- Agalioti, T., S. Lomvardas, B. Parekh, J. Yie, T. Maniatis, and D. Thanos. 2000. Ordered recruitment of chromatin modifying and general transcription factors to the IFN-beta promoter. Cell 103:667-678. - PubMed
-
- Carey, M., and S. T. Smale. 1999. Protocol 3.1, nuclear run-on assay, p. 87. In M. Carey and S. T. Smale (ed.), Transcriptional regulation in eukaryotes. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, N.Y.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
