Tetrameric oligomerization of IkappaB kinase gamma (IKKgamma) is obligatory for IKK complex activity and NF-kappaB activation
- PMID: 12612076
- PMCID: PMC149477
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.23.6.2029-2041.2003
Tetrameric oligomerization of IkappaB kinase gamma (IKKgamma) is obligatory for IKK complex activity and NF-kappaB activation
Abstract
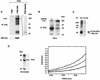
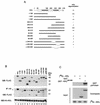
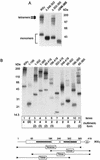
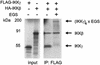
The IkappaB kinase (IKK) complex mediates activation of transcription factor NF-kappaB by phosphorylation of IkappaB proteins. Its catalytic subunits, IKKalpha and IKKbeta, require association with the regulatory IKKgamma (NEMO) component to gain full basal and inducible kinase activity. However, the oligomeric composition of the IKK complex and its regulation by IKKgamma are poorly understood. We show here that IKKgamma predominantly forms tetramers and interacts with IKKalpha or IKKbeta in this state. We propose that tetramerization is accomplished by a prerequisite dimerization through a C-terminal coiled-coil minimal oligomerization domain (MOD). This is followed by dimerization of the dimers with their N-terminal sequences. Tetrameric IKKgamma sequesters four kinase molecules, yielding a gamma(4)(alpha/beta)(4) stoichiometry. Deletion of the MOD leads to loss of tetramerization and of phosphorylation of IKKbeta and IKKgamma, although the kinase can still interact with the resultant IKKgamma monomers and dimers. Likewise, MOD-mediated IKKgamma tetramerization is required to enhance IKKbeta kinase activity when overexpressed in 293 cells and to reconstitute a lipopolysaccharide-responsive IKK complex in pre-B cells. These data thus suggest that IKKgamma tetramerization enforces a spatial positioning of two kinase dimers to facilitate transautophosphorylation and activation.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Regulation and function of IKK and IKK-related kinases.Sci STKE. 2006 Oct 17;2006(357):re13. doi: 10.1126/stke.3572006re13. Sci STKE. 2006. PMID: 17047224 Review.
-
The carboxyl-terminal region of IkappaB kinase gamma (IKKgamma) is required for full IKK activation.Mol Cell Biol. 2002 Sep;22(18):6573-81. doi: 10.1128/MCB.22.18.6573-6581.2002. Mol Cell Biol. 2002. PMID: 12192055 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of I(kappa)B kinase complex by phosphorylation of (gamma)-binding domain of I(kappa)B kinase (beta) by Polo-like kinase 1.J Biol Chem. 2008 Dec 19;283(51):35354-67. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M806258200. Epub 2008 Oct 27. J Biol Chem. 2008. PMID: 18957422 Free PMC article.
-
The zinc finger mutation C417R of I-kappa B kinase gamma impairs lipopolysaccharide- and TNF-mediated NF-kappa B activation through inhibiting phosphorylation of the I-kappa B kinase beta activation loop.J Immunol. 2004 Feb 15;172(4):2446-52. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.172.4.2446. J Immunol. 2004. PMID: 14764716
-
Protein-protein interactions involving IKKgamma (NEMO) that promote the activation of NF-kappaB.J Cell Physiol. 2010 Jun;223(3):558-61. doi: 10.1002/jcp.22105. J Cell Physiol. 2010. PMID: 20301198 Review.
Cited by
-
Structurally plastic NEMO and oligomerization prone IKK2 subunits define the behavior of human IKK2:NEMO complexes in solution.Biochim Biophys Acta Proteins Proteom. 2020 Dec;1868(12):140526. doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2020.140526. Epub 2020 Aug 25. Biochim Biophys Acta Proteins Proteom. 2020. PMID: 32853772 Free PMC article.
-
Parkin interacts with Ambra1 to induce mitophagy.J Neurosci. 2011 Jul 13;31(28):10249-61. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1917-11.2011. J Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 21753002 Free PMC article.
-
The IκB kinase complex in NF-κB regulation and beyond.EMBO Rep. 2014 Jan;15(1):46-61. doi: 10.1002/embr.201337983. Epub 2013 Dec 27. EMBO Rep. 2014. PMID: 24375677 Free PMC article. Review.
-
JNK3 as Therapeutic Target and Biomarker in Neurodegenerative and Neurodevelopmental Brain Diseases.Cells. 2020 Sep 28;9(10):2190. doi: 10.3390/cells9102190. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32998477 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The one thousand and one chaperones of the NF-κB pathway.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2020 Jun;77(12):2275-2288. doi: 10.1007/s00018-019-03402-z. Epub 2019 Dec 6. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2020. PMID: 31811308 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Agou, F., F. Ye, S. Goffinont, G. Courtois, S. Yamaoka, A. Israel, and M. Veron. 2002. NEMO trimerizes through its coiled-coil C-terminal domain. J. Biol. Chem. 277:17464-17475. - PubMed
-
- Behlke, J., and O. Ristau. 2002. A new approximate whole boundary solution of the Lamm differential equation for the analysis of sedimentation velocity experiments. Biophys. Chem. 95:59-68. - PubMed
-
- Behlke, J., O. Ristau, and H. J. Schonfeld. 1997. Nucleotide-dependent complex formation between the Escherichia coli chaperonins GroEL and GroES studied under equilibrium conditions. Biochemistry 36:5149-5156. - PubMed
-
- Cao, Y., G. Bonizzi, T. N. Seagroves, F. R. Greten, R. Johnson, E. V. Schmidt, and M. Karin. 2001. IKKα provides an essential link between RANK signaling and cyclin D1 expression during mammary gland development. Cell 107:763-775. - PubMed
-
- Chen, G., P. Cao, and D. V. Goeddel. 2002. TNF-induced recruitment and activation of the IKK complex require Cdc37 and Hsp90. Mol. Cell 9:401-410. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
