Electrostatic modulation in steroid receptor recruitment of LXXLL and FXXLF motifs
- PMID: 12612084
- PMCID: PMC149467
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.23.6.2135-2150.2003
Electrostatic modulation in steroid receptor recruitment of LXXLL and FXXLF motifs
Abstract
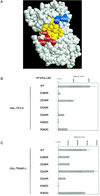
Coactivator recruitment by activation function 2 (AF2) in the steroid receptor ligand binding domain takes place through binding of an LXXLL amphipathic alpha-helical motif at the AF2 hydrophobic surface. The androgen receptor (AR) and certain AR coregulators are distinguished by an FXXLF motif that interacts selectively with the AR AF2 site. Here we show that LXXLL and FXXLF motif interactions with steroid receptors are modulated by oppositely charged residues flanking the motifs and charge clusters bordering AF2 in the ligand binding domain. An increased number of charged residues flanking AF2 in the ligand binding domain complement the two previously characterized charge clamp residues in coactivator recruitment. The data suggest a model whereby coactivator recruitment to the receptor AF2 surface is initiated by complementary charge interactions that reflect a reversal of the acidic activation domain-coactivator interaction model.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Androgen receptor ligand-binding domain interaction and nuclear receptor specificity of FXXLF and LXXLL motifs as determined by L/F swapping.Mol Endocrinol. 2006 Aug;20(8):1742-55. doi: 10.1210/me.2005-0348. Epub 2006 Apr 20. Mol Endocrinol. 2006. PMID: 16627595
-
Distinct recognition modes of FXXLF and LXXLL motifs by the androgen receptor.Mol Endocrinol. 2004 Sep;18(9):2132-50. doi: 10.1210/me.2003-0375. Epub 2004 Jun 3. Mol Endocrinol. 2004. PMID: 15178743
-
Mechanisms of androgen receptor signalling via steroid receptor coactivator-1 in prostate.Endocr Relat Cancer. 2004 Mar;11(1):117-30. doi: 10.1677/erc.0.0110117. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2004. PMID: 15027889
-
Structural features discriminate androgen receptor N/C terminal and coactivator interactions.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2012 Jan 30;348(2):403-10. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2011.03.026. Epub 2011 Jun 1. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2012. PMID: 21664945 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of coactivators and corepressors in the biology and mechanism of action of steroid hormone receptors.J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2000 Jul;5(3):307-24. doi: 10.1023/a:1009503029176. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2000. PMID: 14973393 Review.
Cited by
-
Human checkpoint protein hRad9 functions as a negative coregulator to repress androgen receptor transactivation in prostate cancer cells.Mol Cell Biol. 2004 Mar;24(5):2202-13. doi: 10.1128/MCB.24.5.2202-2213.2004. Mol Cell Biol. 2004. PMID: 14966297 Free PMC article.
-
Perspectives on mechanisms of gene regulation by 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 and its receptor.J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2007 Mar;103(3-5):389-95. doi: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2006.12.050. Epub 2007 Jan 12. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2007. PMID: 17223545 Free PMC article.
-
Epidermal-growth-factor-dependent phosphorylation and ubiquitinylation of MAGE-11 regulates its interaction with the androgen receptor.Mol Cell Biol. 2008 Mar;28(6):1947-63. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01672-07. Epub 2008 Jan 22. Mol Cell Biol. 2008. PMID: 18212060 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of androgen receptor DNA binding activity through direct interaction with the ETS transcription factor ERG.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020 Apr 14;117(15):8584-8592. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1922159117. Epub 2020 Mar 27. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020. PMID: 32220959 Free PMC article.
-
Structural basis for nuclear receptor corepressor recruitment by antagonist-liganded androgen receptor.Mol Cancer Ther. 2008 Oct;7(10):3187-94. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-08-0461. Mol Cancer Ther. 2008. PMID: 18852122 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arriza, J. L., C. Weinberger, G. Cerelli, T. M. Glaser, B. L. Handelin, D. E. Housman, and R. M. Evans. 1987. Cloning of human mineralocorticoid receptor complementary DNA: structural and functional kinship with the glucocorticoid receptor. Science 237:268-275. - PubMed
-
- Bledsoe, R. K., V. G. Montana, T. B. Stanley, C. J. Delves, C. J. Apolito, D. D. McKee, T. G. Consler, D. J. Parks, E. L. Stewart, T. M. Willson, M. H. Lambert, J. T. Moore, K. H. Pearce, and H. E. Xu. 2002. Crystal structure of the glucocorticoid receptor ligand binding domain reveals a novel mode of receptor dimerization and coactivator recognition. Cell 110:93-105. - PubMed
-
- Bradshaw, J. M., R. A. Grucza, J. E. Ladbury, and G. Waksman. 1998. Probing the “two-pronged plug two-holed socket” model for the mechanism of binding of the Src SH2 domain to phosphotyrosyl peptides: a thermodynamic study. Biochemistry 37:9083-9090. - PubMed
-
- Brzozowski, A., A. Pike, Z. Dauter, R. Hubbard, T. Bonn, O. Engstrom, L. Ohman, G. Greene, J. Gustafsson, and M. Carlquist. 1997. Molecular basis of agonism and antagonism in the oestrogen receptor. Nature 389:753-758. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
