The TRE17 oncogene encodes a component of a novel effector pathway for Rho GTPases Cdc42 and Rac1 and stimulates actin remodeling
- PMID: 12612085
- PMCID: PMC149457
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.23.6.2151-2161.2003
The TRE17 oncogene encodes a component of a novel effector pathway for Rho GTPases Cdc42 and Rac1 and stimulates actin remodeling
Abstract
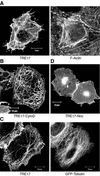
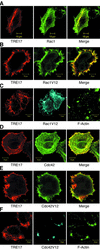
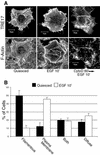
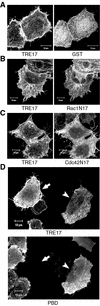
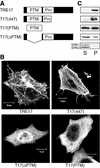
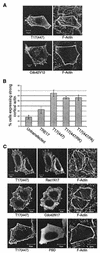
The Rho family GTPases Cdc42 and Rac1 play fundamental roles in transformation and actin remodeling. Here, we demonstrate that the TRE17 oncogene encodes a component of a novel effector pathway for these GTPases. TRE17 coprecipitated specifically with the active forms of Cdc42 and Rac1 in vivo. Furthermore, the subcellular localization of TRE17 was dramatically regulated by these GTPases and mitogens. Under serum-starved conditions, TRE17 localized predominantly to filamentous structures within the cell. Epidermal growth factor (EGF) induced relocalization of TRE17 to the plasma membrane in a Cdc42-/Rac1-dependent manner. Coexpression of activated alleles of Cdc42 or Rac1 also caused complete redistribution of TRE17 to the plasma membrane, where it partially colocalized with the GTPases in filopodia and ruffles, respectively. Membrane recruitment of TRE17 by EGF or the GTPases was dependent on actin polymerization. Finally, we found that a C-terminal truncation mutant of TRE17 induced the accumulation of cortical actin, mimicking the effects of activated Cdc42. Together, these results identify TRE17 as part of a novel effector complex for Cdc42 and Rac1, potentially contributing to their effects on actin remodeling. The present study provides insights into the regulation and cellular function of this previously uncharacterized oncogene.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Vav2 activates Rac1, Cdc42, and RhoA downstream from growth factor receptors but not beta1 integrins.Mol Cell Biol. 2000 Oct;20(19):7160-9. doi: 10.1128/MCB.20.19.7160-7169.2000. Mol Cell Biol. 2000. PMID: 10982832 Free PMC article.
-
Cdc42/Rac1-dependent activation of the p21-activated kinase (PAK) regulates human platelet lamellipodia spreading: implication of the cortical-actin binding protein cortactin.Blood. 2002 Dec 15;100(13):4462-9. doi: 10.1182/blood.V100.13.4462. Blood. 2002. PMID: 12453877
-
IQGAP2 functions as a GTP-dependent effector protein in thrombin-induced platelet cytoskeletal reorganization.Blood. 2003 Apr 15;101(8):3021-8. doi: 10.1182/blood-2002-09-2807. Epub 2002 Dec 19. Blood. 2003. PMID: 12515716
-
Ras-related GTPases and the cytoskeleton.Mol Biol Cell. 1992 May;3(5):475-9. doi: 10.1091/mbc.3.5.475. Mol Biol Cell. 1992. PMID: 1611153 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cell motility: can Rho GTPases and microtubules point the way?J Cell Sci. 2001 Nov;114(Pt 21):3795-803. doi: 10.1242/jcs.114.21.3795. J Cell Sci. 2001. PMID: 11719546 Review.
Cited by
-
The TBC (Tre-2/Bub2/Cdc16) domain protein TRE17 regulates plasma membrane-endosomal trafficking through activation of Arf6.Mol Cell Biol. 2004 Nov;24(22):9752-62. doi: 10.1128/MCB.24.22.9752-9762.2004. Mol Cell Biol. 2004. PMID: 15509780 Free PMC article.
-
USP6 activation in nodular fasciitis by promoter-swapping gene fusions.Mod Pathol. 2017 Nov;30(11):1577-1588. doi: 10.1038/modpathol.2017.78. Epub 2017 Jul 28. Mod Pathol. 2017. PMID: 28752842
-
Atypical mechanism of NF-κB activation by TRE17/ubiquitin-specific protease 6 (USP6) oncogene and its requirement in tumorigenesis.Oncogene. 2012 Jul 26;31(30):3525-35. doi: 10.1038/onc.2011.520. Epub 2011 Nov 14. Oncogene. 2012. PMID: 22081069 Free PMC article.
-
Deubiquitinase activities required for hepatocyte growth factor-induced scattering of epithelial cells.Curr Biol. 2009 Sep 15;19(17):1463-6. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2009.07.040. Epub 2009 Aug 20. Curr Biol. 2009. PMID: 19699092 Free PMC article.
-
Virus Control of Trafficking from Sorting Endosomes.mBio. 2018 Jul 24;9(4):e00683-18. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00683-18. mBio. 2018. PMID: 30042195 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Albert, S., and D. Gallwitz. 1999. Two new members of a family of Ypt/Rab GTPase activating proteins: promiscuity of substrate recognition. J. Biol. Chem. 274:33186-33189. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
