NPR1 modulates cross-talk between salicylate- and jasmonate-dependent defense pathways through a novel function in the cytosol
- PMID: 12615947
- PMCID: PMC150028
- DOI: 10.1105/tpc.009159
NPR1 modulates cross-talk between salicylate- and jasmonate-dependent defense pathways through a novel function in the cytosol
Abstract
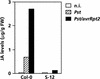
Plant defenses against pathogens and insects are regulated differentially by cross-communicating signal transduction pathways in which salicylic acid (SA) and jasmonic acid (JA) play key roles. In this study, we investigated the molecular mechanism of the antagonistic effect of SA on JA signaling. Arabidopsis plants unable to accumulate SA produced 25-fold higher levels of JA and showed enhanced expression of the JA-responsive genes LOX2, PDF1.2, and VSP in response to infection by Pseudomonas syringae pv tomato DC3000, indicating that in wild-type plants, pathogen-induced SA accumulation is associated with the suppression of JA signaling. Analysis of the Arabidopsis mutant npr1, which is impaired in SA signal transduction, revealed that the antagonistic effect of SA on JA signaling requires the regulatory protein NPR1. Nuclear localization of NPR1, which is essential for SA-mediated defense gene expression, is not required for the suppression of JA signaling, indicating that cross-talk between SA and JA is modulated through a novel function of NPR1 in the cytosol.
Figures


References
-
- Aoyama, T., and Chua, N.H. (1997). A glucocorticoid-mediated transcriptional induction system in transgenic plants. Plant J. 11, 605–612. - PubMed
-
- Aravind, L., and Koonin, E.V. (1999). Fold prediction and evolutionary analysis of the POZ domain: Structural and evolutionary relationship with the potassium channel tetramerization domain. J. Mol. Biol. 285, 1353–1361. - PubMed
-
- Baldwin, A.S. (1996). The NF-κB and IκB proteins: New discoveries and insights. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 14, 649–683. - PubMed
-
- Berger, S., Bell, E., Sadka, A., and Mullet, J.E. (1995). Arabidopsis thaliana Atvsp is homologous to soybean VspA and VspB, genes encoding vegetative storage protein acid phosphatases, and is regulated similarly by methyl jasmonate, wounding, sugars, light and phosphate. Plant Mol. Biol. 27, 933–942. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

