Linkage of beta1-adrenergic stimulation to apoptotic heart cell death through protein kinase A-independent activation of Ca2+/calmodulin kinase II
- PMID: 12618516
- PMCID: PMC151893
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI16326
Linkage of beta1-adrenergic stimulation to apoptotic heart cell death through protein kinase A-independent activation of Ca2+/calmodulin kinase II
Abstract
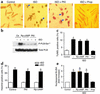
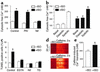
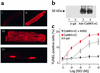
beta(1)-adrenergic receptor (beta(1)AR) stimulation activates the classic cAMP/protein kinase A (PKA) pathway to regulate vital cellular processes from the change of gene expression to the control of metabolism, muscle contraction, and cell apoptosis. Here we show that sustained beta(1)AR stimulation promotes cardiac myocyte apoptosis by activation of Ca(2+)/calmodulin kinase II (CaMKII), independently of PKA signaling. beta(1)AR-induced apoptosis is resistant to inhibition of PKA by a specific peptide inhibitor, PKI14-22, or an inactive cAMP analogue, Rp-8-CPT-cAMPS. In contrast, the beta(1)AR proapoptotic effect is associated with non-PKA-dependent increases in intracellular Ca(2+) and CaMKII activity. Blocking the L-type Ca(2+) channel, buffering intracellular Ca(2+), or inhibiting CaMKII activity fully protects cardiac myocytes against beta(1)AR-induced apoptosis, and overexpressing a cardiac CaMKII isoform, CaMKII-deltaC, markedly exaggerates the beta(1)AR apoptotic effect. These findings indicate that CaMKII constitutes a novel PKA-independent linkage of beta(1)AR stimulation to cardiomyocyte apoptosis that has been implicated in the overall process of chronic heart failure.
Figures



Comment in
-
Calcium and the heart: a question of life and death.J Clin Invest. 2003 Mar;111(5):597-600. doi: 10.1172/JCI18067. J Clin Invest. 2003. PMID: 12618512 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Dohlman HG, Thorner J, Caron MG, Lefkowitz RJ. Model systems for the study of seven-transmembrane-segment receptors. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1991;60:653–688. - PubMed
-
- Xiao RP. β-adrenergic signaling in the heart: dual coupling of the β2-adrenergic receptor to Gs and Gi proteins. Sci. STKE. 2001;104:RE15. - PubMed
-
- Zaugg M, et al. β-adrenergic receptor subtypes differentially affect apoptosis in adult rat ventricular myocytes. Circulation. 2000;102:344–350. - PubMed
-
- Communal C, Singh K, Sawyer DB, Colucci WS. Opposing effects of β1- and β2-adrenergic receptors on cardiac myocyte apoptosis: role of a pertussis toxin-sensitive G protein. Circulation. 1999;100:2210–2212. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

