Induction of neuropilin-1 and vascular endothelial growth factor by epidermal growth factor in human gastric cancer cells
- PMID: 12618892
- PMCID: PMC2376351
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6600811
Induction of neuropilin-1 and vascular endothelial growth factor by epidermal growth factor in human gastric cancer cells
Abstract
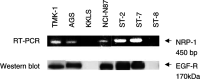
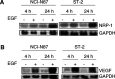
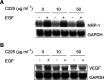
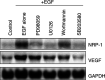
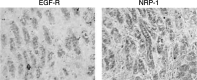
The epidermal growth factor receptor (EGF-R) pathway plays a pivotal role in the progression of human gastric cancer. The angiogenic factor vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) has been shown to be induced by EGF in various cancer cell lines. Neuropilin-1 (NRP-1) acts as a coreceptor for VEGF-165 and increases its affinity for VEGF receptor 2 (VEGFR-2) in endothelial cells. Furthermore, NRP-1 has been found to be expressed by tumour cells and has been shown to enhance tumour angiogenesis and growth in preclinical models. We examined the expression of NRP-1 mRNA and EGF-R protein in seven human gastric cancer cell lines. NRP-1 expression was expressed in five of seven cell lines, and EGF-R expression closely mirrored NRP-1 expression. Moreover, in EGF-R-positive NCI-N87 and ST-2 cells, EGF induced both NRP-1 and VEGF mRNA expression. C225, a monoclonal antibody to EGF-R, blocked EGF-induced NRP-1 and VEGF expression in NCI-N87 cells in a dose-dependent manner. The treatment of NCI-N87 cells with EGF resulted in increases in phosphorylation of Erk1/2, Akt, and P38. Blockade of the Erk, phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase/Akt, or P38 pathways in this cell line prevented EGF induction of NRP-1 and VEGF. These results suggest that regulation of NRP-1 expression in human gastric cancer is intimately associated with the EGF/EGF-R system. Activation of EGF-R might contribute to gastric cancer angiogenesis by a mechanism that involves upregulation of VEGF and NRP-1 expression via multiple signalling pathways.
Figures

References
-
- Akagi Y, Liu W, Zebrowski B, Xie K, Ellis LM (1998) Regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor expression in human colon cancer by insulin-like growth factor-I. Cancer Res 58: 4008–4014 - PubMed
-
- Bachelder RE, Crago A, Chung J, Wendt MA, Shaw LM, Robinson G, Mercurio AM (2001) Vascular endothelial growth factor is an autocrine survival factor for neuropilin-expressing breast carcinoma cells. Cancer Res 61: 5736–5740 - PubMed
-
- Basque JR, Chenard M, Chailler P, Menard D (2001) Gastric cancer cell lines as models to study human digestive functions. J Cell Biochem 81: 241–251 - PubMed
-
- Bruns CJ, Harbison MT, Davis DW, Portera CA, Tsan R, McConkey DJ, Evans DB, Abbruzzese JL, Hicklin DJ, Radinsky R (2000) Epidermal growth factor receptor blockade with C225 plus gemcitabine results in regression of human pancreatic carcinoma growing orthotopically in nude mice by antiangiogenic mechanisms. Clin Cancer Res 6: 1936–1948 - PubMed
-
- Ciardiello F, Bianco R, Damiano V, Fontanini G, Caputo R, Pomatico G, De Placido S, Bianco AR, Mendelsohn J, Tortora G (2000) Antiangiogenic and antitumour activity of anti-epidermal growth factor receptor C225 monoclonal antibody in combination with vascular endothelial growth factor antisense oligonucleotide in human GEO colon cancer cells. Clin Cancer Res 6: 3739–3747 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

