Musculoskeletal deterioration and hemicorporectomy after spinal cord injury
- PMID: 12620090
- PMCID: PMC4042312
Musculoskeletal deterioration and hemicorporectomy after spinal cord injury
Abstract
Background and purpose: The long-term management following an hemicorporectomy (HCP) is not well documented in the scientific literature. The purpose of this case report is to describe the 25-year history of a man with a spinal cord injury who experienced severe musculoskeletal deterioration and hemicorporectomy.
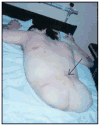
Case description: The client sustained T10 complete paraplegia at age 18 years, developed severe decubitus ulcers, and required an HCP as a life-saving measure 13 years later. The authors describe the chronology of several rehabilitation and prosthetic strategies and speculate on factors that may have contributed to their successes and failures.
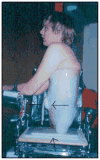
Outcomes: The client survived 12 years after the HCP and returned to independent mobility, self-care, and schooling despite complications with continued skin breakdown. Over the 12 years following discharge from the hospital after the spinal cord injury, he spent 749 days in the hospital. During the 12 years he lived after discharge from the hospital following the HCP, he was hospitalized 190 days.
Discussion: The authors discuss factors contributing to the client's musculoskeletal deterioration including chronic wounds, postural deviations, and incomplete adherence to pressure-relief recommendations and raise considerations for physical therapists who treat patients after HCP.
Figures


References
-
- Weaver JM, Flynn MB. Hemicorporectomy. J Surg Oncol. 2000;73(suppl):117–124. - PubMed
-
- Aust JB, Page CP. Hemicorporectomy. J Surg Oncol. 1985;30:226–230. - PubMed
-
- Terz JJ, Schaffner MJ, Goodkin R, et al. Translumbar amputation. Cancer. 1990;65:2668–2675. - PubMed
-
- Ferrara BE. Hemicorporectomy: a collective review. J Surg Oncol. 1990;45:270–278. - PubMed
-
- Baker TC, Berkowitz T, Lord GB, Hankins HV. Hemicorporectomy. Br J Surg. 1970;57:471– 476. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
