Quorum-sensing system and stationary-phase sigma factor (rpoS) of the onion pathogen Burkholderia cepacia genomovar I type strain, ATCC 25416
- PMID: 12620866
- PMCID: PMC150111
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.69.3.1739-1747.2003
Quorum-sensing system and stationary-phase sigma factor (rpoS) of the onion pathogen Burkholderia cepacia genomovar I type strain, ATCC 25416
Abstract
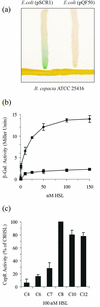
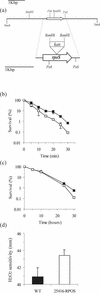
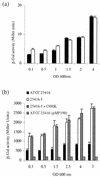
Bacterial strains belonging to Burkholderia cepacia can be human opportunistic pathogens, plant pathogens, and plant growth promoting and have remarkable catabolic activity. B. cepacia consists of several genomovars comprising what is now known as the B. cepacia complex. Here we report the quorum-sensing system of a genomovar I onion rot type strain ATCC 25416. Quorum sensing is a cell-density-dependent regulatory response which involves the production of N-acyl homoserine lactone (HSL) signal molecules. The cep locus has been inactivated in the chromosome, and it has been shown that CepI is responsible for the biosynthesis of an N-hexanoyl HSL (C(6)-HSL) and an N-octanoyl HSL (C(8)-HSL) and that the cep locus regulates protease production as well as onion pathogenicity via the expression of a secreted polygalacturonase. A cep-lacZ-based sensor plasmid has been constructed and used to demonstrate that CepR responded to C(6)-HSL with only 15% of the molar efficiency of C(8)-HSL, that a cepR knockout mutant synthesized 70% less HSLs, and that CepR responded best towards long-chain HSLs. In addition, we also report the cloning and characterization of the stationary-phase sigma factor gene rpoS of B. cepacia ATCC 25416. It was established that quorum sensing in B. cepacia has a negative effect on rpoS expression as determined by using an rpoS-lacZ transcriptional fusion; on the other hand, rpoS-null mutants displayed no difference in the accumulation of HSL signal molecules.
Figures

References
-
- Beringer, J. E., J. L. Beynon, A. V. Buchanan-Wollaston, and A. W. B. Jonhston. 1978. Transfer of the drug-resistance transposon Tn5 to Rhizobium. Nature 276:633-634.
-
- Better, M., B. Lewis, D. Corbin, G. Ditta, and D. R. Helinski. 1983. Structural relationships among Rhizobium meliloti symbiotic promoters. Cell 35:479-485. - PubMed
-
- Bevivino, A., S. Tabacchioni, L. Chiarini, M. V. Carusi, M. Del Gallo, and P. Visca. 1994. Phenotypic comparison between rhizosphere and clinical isolates of Burkholderia cepacia. Microbiology 140:1069-1077. - PubMed
-
- Birnboim, H. C. 1983. A rapid alkaline extraction method for the isolation of plasmid DNA. Methods Enzymol. 100:243-255. - PubMed
-
- Burkholder, W. 1950. Sour skin, a bacterial rot of onions bulbs. Phytopathology 40:115-118.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

