Heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor and ErbB signaling is essential for heart function
- PMID: 12621152
- PMCID: PMC152273
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0537588100
Heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor and ErbB signaling is essential for heart function
Abstract
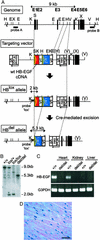
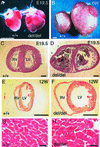
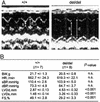
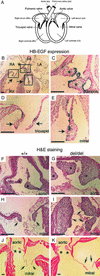
The heparin-binding epidermal growth factor (EGF)-like growth factor (HB-EGF) is a member of the EGF family of growth factors that binds to and activates the EGF receptor (EGFR) and the related receptor tyrosine kinase, ErbB4. HB-EGF-null mice (HB(del/del)) were generated to examine the role of HB-EGF in vivo. More than half of the HB(del/del) mice died in the first postnatal week. The survivors developed severe heart failure with grossly enlarged ventricular chambers. Echocardiographic examination showed that the ventricular chambers were dilated and that cardiac function was diminished. Moreover, HB(del/del) mice developed grossly enlarged cardiac valves. The cardiac valve and the ventricular chamber phenotypes resembled those displayed by mice lacking EGFR, a receptor for HB-EGF, and by mice conditionally lacking ErbB2, respectively. HB-EGF-ErbB interactions in the heart were examined in vivo by administering HB-EGF to WT mice. HB-EGF induced tyrosine phosphorylation of ErbB2 and ErbB4, and to a lesser degree, of EGFR in cardiac myocytes. In addition, constitutive tyrosine phosphorylation of both ErbB2 and ErbB4 was significantly reduced in HB(del/del) hearts. It was concluded that HB-EGF activation of receptor tyrosine kinases is essential for normal heart function.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Defective valvulogenesis in HB-EGF and TACE-null mice is associated with aberrant BMP signaling.EMBO J. 2003 Jun 2;22(11):2704-16. doi: 10.1093/emboj/cdg264. EMBO J. 2003. PMID: 12773386 Free PMC article.
-
Heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor interacts with mouse blastocysts independently of ErbB1: a possible role for heparan sulfate proteoglycans and ErbB4 in blastocyst implantation.Development. 1999 May;126(9):1997-2005. doi: 10.1242/dev.126.9.1997. Development. 1999. PMID: 10101133
-
ErbB and HB-EGF signaling in heart development and function.Cell Struct Funct. 2006;31(1):1-14. doi: 10.1247/csf.31.1. Cell Struct Funct. 2006. PMID: 16508205 Review.
-
HB-EGF promotes epithelial cell migration in eyelid development.Development. 2005 Oct;132(19):4317-26. doi: 10.1242/dev.02030. Epub 2005 Sep 1. Development. 2005. PMID: 16141218
-
Heparin-binding epidermal growth factor-like growth factor as a novel targeting molecule for cancer therapy.Cancer Sci. 2006 May;97(5):341-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2006.00188.x. Cancer Sci. 2006. PMID: 16630129 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Mechanisms of implantation: strategies for successful pregnancy.Nat Med. 2012 Dec;18(12):1754-67. doi: 10.1038/nm.3012. Nat Med. 2012. PMID: 23223073 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Essential roles of heparin-binding epidermal growth factor-like growth factor in the brain.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2012 Oct;18(10):803-10. doi: 10.1111/j.1755-5949.2012.00371.x. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2012. PMID: 23006514 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Valvulogenesis: the moving target.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2007 Aug 29;362(1484):1489-503. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2007.2130. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2007. PMID: 17569640 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor by miR-212 and acquired cetuximab-resistance in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.PLoS One. 2010 Sep 13;5(9):e12702. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0012702. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 20856931 Free PMC article.
-
Myeloid Cell-Derived HB-EGF Drives Tissue Recovery After Pancreatitis.Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019;8(2):173-192. doi: 10.1016/j.jcmgh.2019.05.006. Epub 2019 May 21. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019. PMID: 31125624 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

