Transfection of IL-10 expression vectors into endothelial cultures attenuates alpha4beta7-dependent lymphocyte adhesion mediated by MAdCAM-1
- PMID: 12625840
- PMCID: PMC151603
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-230x-3-3
Transfection of IL-10 expression vectors into endothelial cultures attenuates alpha4beta7-dependent lymphocyte adhesion mediated by MAdCAM-1
Abstract
Background: Enhanced expression of MAdCAM-1 (mucosal addressin cell adhesion molecule-1) is associated with the onset and progression of inflammatory bowel disease. The clinical significance of elevated MAdCAM-1 expression is supported by studies showing that immunoneutralization of MAdCAM-1, or its ligands reduce inflammation and mucosal damage in models of colitis. Interleukin-10 (IL-10) is an endogenous anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory cytokine that has been shown to prevent inflammation and injury in several animal studies, however clinical IL-10 treatment remains insufficient because of difficulties in the route of IL-10 administration and its biological half-life. Here, we examined the ability of introducing an IL-10 expression vector into endothelial cultures to reduce responses to a proinflammatory cytokine, TNF-alpha
Methods: A human IL-10 expression vector was transfected into high endothelial venular ('HEV') cells (SVEC4-10); we then examined TNF-alpha induced lymphocyte adhesion to lymphatic endothelial cells and TNF-alpha induced expression of MAdCAM-1 and compared these responses to control monolayers.
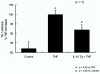
Results: Transfection of the IL-10 vector into endothelial cultures significantly reduced TNF-alpha induced, MAdCAM-1 dependent lymphocyte adhesion (compared to non-transfected cells). IL-10 transfected endothelial cells expressed less than half (46 +/- 6.6%) of the MAdCAM-1 induced by TNF-alpha (set as 100%) in non-transfected (control) cells.
Conclusion: Our results suggest that gene therapy of the gut microvasculature with IL-10 vectors may be useful in the clinical treatment of IBD.
Figures


References
-
- Granger DN, Kubes P. The microcirculation and inflammation: modulation of leukocyte-endothelial cell adhesion. J Leukoc Biol. 1994;55:662–675. - PubMed
-
- Connor EM, Eppihimer MJ, Morise Z, Granger DN, Grisham MB. Expression of mucosal addressin cell adhesion molecule-1 (MAdCAM-1) in acute and chronic inflammation. J Leukoc Biol. 1999;65:349–355. - PubMed
-
- Shigematsu T, Specian RD, Wolf RE, Grisham MB, Granger DN. MAdCAM mediates lymphocyte-endothelial cell adhesion in a murine model of chronic colitis. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2001;281:G1309–G1315. - PubMed
-
- Oshima T, Pavlick K, Grisham MB, Jordan P, Manas K, Joh T, et al. Glucocorticoids and IL-10, but not 6-MP, 5-ASA or sulfasalazine block endothelial expression of MAdCAM-1: implications for inflammatory bowel disease therapy. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2001;15:1211–1218. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2036.2001.01048.x. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

