Glycosaminoglycans in human retinoblastoma cells: heparan sulfate, a modulator of the pigment epithelium-derived factor-receptor interactions
- PMID: 12625842
- PMCID: PMC151665
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2091-4-1
Glycosaminoglycans in human retinoblastoma cells: heparan sulfate, a modulator of the pigment epithelium-derived factor-receptor interactions
Abstract
Background: Pigment epithelium-derived factor (PEDF) has binding affinity for cell-surface receptors in retinoblastoma cells and for glycosaminoglycans. We investigated the effects of glycosaminoglycans on PEDF-receptor interactions.
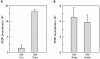
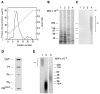
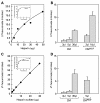
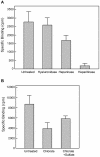
Results: 125I-PEDF formed complexes with protease-resistant components of medium conditioned by human retinoblastoma Y-79 cells. Using specific glycosaminoglycan degrading enzymes in spectrophotometric assays and PEDF-affinity chromatography, we detected heparin and heparan sulfate-like glycosaminoglycans in the Y-79 conditioned media, which had binding affinity for PEDF. The Y-79 conditioned media significantly enhanced the binding of 125I-PEDF to Y-79 cell-surface receptors. However, enzymatic and chemical depletion of sulfated glycosaminoglycans from the Y-79 cell cultures by heparitinase and chlorate treatments decreased the degree of 125I-PEDF binding to cell-surface receptors.
Conclusions: These data indicate that retinoblastoma cells secrete heparin/heparan sulfate with binding affinity for PEDF, which may be important in efficient cell-surface receptor binding.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

