Serological cross-reactivities between antibodies to simian virus 40, BK virus, and JC virus assessed by virus-like-particle-based enzyme immunoassays
- PMID: 12626455
- PMCID: PMC150538
- DOI: 10.1128/cdli.10.2.278-285.2003
Serological cross-reactivities between antibodies to simian virus 40, BK virus, and JC virus assessed by virus-like-particle-based enzyme immunoassays
Abstract
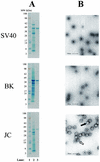
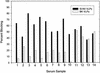
Enzyme immunoassays (EIAs) for detection of serum antibodies to simian virus 40 (SV40), BK virus (BKV), and JC virus (JCV) were developed by using virus-like-particles (VLPs) produced in insect cells from recombinant baculoviruses expressing the VP1 protein of the respective virus. Rhesus macaque sera with neutralizing antibodies to SV40 showed a high level of reactivity in the SV40 VLP-based EIA, and these sera also showed lower levels of reactivity in the BKV and JCV VLP-based EIAs. Rhesus macaque sera negative for neutralizing antibodies to SV40 were negative in all three EIAs. Competitive binding assays showed that SV40 VLPs inhibited BKV reactivity. In rhesus macaque sera, high optical density (OD) values for antibodies to SV40 VLPs were correlated with high OD values for antibodies to BKV but not with high OD values for antibodies to JCV VLPs. Human sera with neutralizing antibodies to SV40 were more reactive to SV40 VLPs than human sera without neutralizing antibodies to SV40. The greater SV40 reactivities of human sera were correlated with greater reactivities to BKV VLPs but not JCV VLPs. These data suggest that cross-reactivity with BKV antibodies may account for part of the low-level SV40 reactivity seen in human sera. With their greater versatility and their suitability for large-scale testing, the VLP-based EIAs for SV40, BKV, and JCV are likely to contribute to a better understanding of the biology of these viruses.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Serological cross reactivity between polyomavirus capsids.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2006;577:73-84. doi: 10.1007/0-387-32957-9_5. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2006. PMID: 16626028 Review.
-
Comparison of antibody titers determined by hemagglutination inhibition and enzyme immunoassay for JC virus and BK virus.J Clin Microbiol. 2000 Jan;38(1):105-9. doi: 10.1128/JCM.38.1.105-109.2000. J Clin Microbiol. 2000. PMID: 10618072 Free PMC article.
-
Population-based study of antibody to the human polyomaviruses BKV and JCV and the simian polyomavirus SV40.J Med Virol. 2003 Sep;71(1):115-23. doi: 10.1002/jmv.10450. J Med Virol. 2003. PMID: 12858417
-
Serological diagnosis of human polyomavirus infection.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2006;577:96-101. doi: 10.1007/0-387-32957-9_7. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2006. PMID: 16626030 Review.
-
Lack of serologic evidence for prevalent simian virus 40 infection in humans.J Natl Cancer Inst. 2003 Oct 15;95(20):1522-30. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djg074. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2003. PMID: 14559874
Cited by
-
Complete nucleotide sequence of polyomavirus SA12.J Virol. 2005 Oct;79(20):13094-104. doi: 10.1128/JVI.79.20.13094-13104.2005. J Virol. 2005. PMID: 16189011 Free PMC article.
-
An SV40 VP1-derived epitope recognized by CD8+ T cells is naturally processed and presented by HLA-A*0201 and cross-reactive with human polyomavirus determinants.Virology. 2008 Jun 20;376(1):183-90. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2008.02.033. Epub 2008 Apr 10. Virology. 2008. PMID: 18402997 Free PMC article.
-
Prospective study of JC virus seroreactivity and the development of colorectal cancers and adenomas.Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2009 May;18(5):1515-23. doi: 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-08-1119. Epub 2009 Apr 21. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2009. PMID: 19383887 Free PMC article.
-
Immune System Involvement in the Pathogenesis of JC Virus Induced PML: What is Learned from Studies of Patients with Underlying Diseases and Therapies as Risk Factors.Front Immunol. 2015 Apr 28;6:159. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2015.00159. eCollection 2015. Front Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25972864 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cross-reactivity of T lymphocytes recognizing a human cytotoxic T-lymphocyte epitope within BK and JC virus VP1 polypeptides.J Virol. 2005 Sep;79(17):11170-8. doi: 10.1128/JVI.79.17.11170-11178.2005. J Virol. 2005. PMID: 16103168 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bergsagel, D. J., M. J. Finegold, J. S. Butel, W. J. Kupsky, and R. L. Garcea. 1992. DNA sequences similar to those of simian virus 40 in ependymomas and choroid plexus tumors of childhood. N. Engl. J. Med. 326:988-993. - PubMed
-
- Brown, P., T. Tsai, and D. C. Gajdusek. 1975. Seroepidemiology of human papovaviruses. Discovery of virgin populations and some unusual patterns of antibody prevalence among remote peoples of the world. Am. J. Epidemiol. 102:331-340. - PubMed
-
- Butel, J. S., S. Jafar, C. Wong, A. S. Arrington, A. R. Opekun, M. J. Finegold, and E. Adam. 1999. Evidence of SV40 infections in hospitalized children. Hum. Pathol. 30:1496-1502. - PubMed
-
- Carbone, M., H. I. Pass, P. Rizzo, M. Marinetti, M. Di Muzio, D. J. Mew, A. S. Levine, and A. Procopio. 1994. Simian virus 40-like DNA sequences in human pleural mesothelioma. Oncogene 9:1781-1790. - PubMed
-
- Carbone, M., P. Rizzo, A. Procopio, M. Giuliano, H. I. Pass, M. C. Gebhardt, C. Mangham, M. Hansen, D. F. Malkin, G. Bushart, F. Pompetti, P. Picci, A. S. Levine, J. D. Bergsagel, and R. L. Garcea. 1996. SV40-like sequences in human bone tumors. Oncogene 13:527-535. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

