Grb2 regulates internalization of EGF receptors through clathrin-coated pits
- PMID: 12631709
- PMCID: PMC151565
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e02-08-0532
Grb2 regulates internalization of EGF receptors through clathrin-coated pits
Abstract
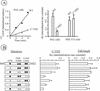
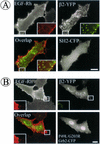
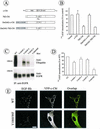
The molecular mechanisms of clathrin-dependent internalization of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) are not well understood and, in particular, the sequence motifs that mediate EGFR interactions with coated pits have not been mapped. We generated a panel of EGFR mutants and stably expressed these mutants in porcine aortic endothelial (PAE) cells. Interestingly, mutations of tyrosine phosphorylation sites 1068 and 1086 that interact with growth-factor-receptor-binding protein Grb2 completely abolished receptor internalization in PAE cells. Quantitative analysis of colocalization of EGF-rhodamine conjugate and coated pits labeled with yellow-fluorescent-protein-tagged beta2 subunit of clathrin adaptor complex AP-2 revealed that EGFR mutants lacking Grb2 binding sites do not efficiently enter coated pits. The depletion of Grb2 from PAE as well as HeLa cells expressing endogenous EGFRs by RNA interference substantially reduced the rate of EGFR internalization through clathrin-dependent pathway, thus providing the direct evidence for the important role of Grb2 in this process. Overexpression of Grb2 mutants, in which the SH3 domains were either deleted or inactivated by point mutations, significantly inhibited EGFR internalization in both PAE and HeLa cells. These findings indicate that Grb2, in addition to its key function in signaling through Ras, has a major regulatory role at the initial steps of EGFR internalization through clathrin-coated pits. Furthermore, the EGFR mutant lacking Grb2 binding sites did not efficiently recruit c-Cbl and was not polyubiquitinated. The data are consistent with the model whereby Grb2 participates in EGFR internalization through the recruitment of Cbl to the receptor, thus allowing proper ubiquitylation of EGFR and/or associated proteins at the plasma membrane.
Figures






References
-
- Alvarez CV, Shon K-J, Miloso M, Beguinot L. Structural requirements of the epidermal growth factor receptor for tyrosine phosphorylation of eps8 and eps15, substrates lacking Src SH2 homology domains. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:16271–16276. - PubMed
-
- Beguinot L, Werth D, Ito S, Richert N, Willingham MC, Pastan I. Functional studies on the EGF receptor with an antibody that recognizes the intracellular portion of the receptor. J Biol Chem. 1986;261:1801–1807. - PubMed
-
- Carter RE, Sorkin A. Endocytosis of functional epidermal growth factor receptor- green fluorescent protein chimera. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:35000–35007. - PubMed
-
- Chang C-P, Kao JPY, Lazar CS, Walsh BJ, Wells A, Wiley HS, Gill GN, Rosenfeld MG. Ligand-induced internalization and increased cell calcium are Mediated via distinct structural elements in the carboxyl terminus of the epidermal growth factor receptor. J Biol Chem. 1991;266:23467–23470. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

