KDEL and KKXX retrieval signals appended to the same reporter protein determine different trafficking between endoplasmic reticulum, intermediate compartment, and Golgi complex
- PMID: 12631711
- PMCID: PMC151567
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e02-08-0468
KDEL and KKXX retrieval signals appended to the same reporter protein determine different trafficking between endoplasmic reticulum, intermediate compartment, and Golgi complex
Abstract
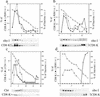
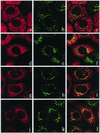
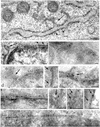
Many endoplasmic reticulum (ER) proteins maintain their residence by dynamic retrieval from downstream compartments of the secretory pathway. In previous work we compared the retrieval process mediated by the two signals, KKMP and KDEL, by appending them to the same neutral reporter protein, CD8, and found that the two signals determine a different steady-state localization of the reporter. CD8-K (the KDEL-bearing form) was restricted mainly to the ER, whereas CD8-E19 (the KKMP-bearing form) was distributed also to the intermediate compartment and Golgi complex. To investigate whether this different steady-state distribution reflects a difference in exit rates from the ER and/or in retrieval, we have now followed the first steps of export of the two constructs from the ER and their trafficking between ER and Golgi complex. Contrary to expectation, we find that CD8-K is efficiently recruited into transport vesicles, whereas CD8-E19 is not. Thus, the more restricted ER localization of CD8-K must be explained by a more efficient retrieval to the ER. Moreover, because most of ER resident CD8-K is not O-glycosylated but almost all CD8-E19 is, the results suggest that CD8-K is retrieved from the intermediate compartment, before reaching the Golgi, where O-glycosylation begins. These results illustrate how different retrieval signals determine different trafficking patterns and pose novel questions on the underlying molecular mechanisms.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Different fate of a single reporter protein containing KDEL or KKXX targeting signals stably expressed in mammalian cells.J Biol Chem. 1996 Feb 16;271(7):3541-7. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.7.3541. J Biol Chem. 1996. PMID: 8631959
-
A different intracellular distribution of a single reporter protein is determined at steady state by KKXX or KDEL retrieval signals.J Biol Chem. 1999 Apr 9;274(15):10413-20. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.15.10413. J Biol Chem. 1999. PMID: 10187831
-
Retrograde transport of KDEL-bearing B-fragment of Shiga toxin.J Biol Chem. 1997 Aug 1;272(31):19554-61. doi: 10.1074/jbc.272.31.19554. J Biol Chem. 1997. PMID: 9235960
-
ER-to-Golgi transport and cytoskeletal interactions in animal cells.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2004 Jan;61(2):133-45. doi: 10.1007/s00018-003-3352-9. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2004. PMID: 14745493 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Retention and retrieval in the endoplasmic reticulum and the Golgi apparatus.Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1994 Aug;6(4):517-21. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(94)90070-1. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1994. PMID: 7986527 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Opposing USP19 splice variants in TGF-β signaling and TGF-β-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition of breast cancer cells.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2023 Jan 17;80(2):43. doi: 10.1007/s00018-022-04672-w. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2023. PMID: 36646950 Free PMC article.
-
Nef binds p6* in GagPol during replication of human immunodeficiency virus type 1.J Virol. 2004 May;78(10):5311-23. doi: 10.1128/jvi.78.10.5311-5323.2004. J Virol. 2004. PMID: 15137387 Free PMC article.
-
Biochemical evidence of the interactions of membrane type-1 matrix metalloproteinase (MT1-MMP) with adenine nucleotide translocator (ANT): potential implications linking proteolysis with energy metabolism in cancer cells.Biochem J. 2009 Apr 28;420(1):37-47. doi: 10.1042/BJ20090082. Biochem J. 2009. PMID: 19232058 Free PMC article.
-
The Perlman syndrome DIS3L2 exoribonuclease safeguards endoplasmic reticulum-targeted mRNA translation and calcium ion homeostasis.Nat Commun. 2020 May 26;11(1):2619. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-16418-y. Nat Commun. 2020. PMID: 32457326 Free PMC article.
-
Proteolytic cleavage is required for functional neuroligin 2 maturation and trafficking in Drosophila.J Mol Cell Biol. 2017 Jun 1;9(3):231-242. doi: 10.1093/jmcb/mjx015. J Mol Cell Biol. 2017. PMID: 28498949 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Andersson H, Kappeler F, Hauri HP. Protein targeting to endoplasmic reticulum by dilysine signals involves direct retention in addition to retrieval. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:15080–15084. - PubMed
-
- Bonatti S, Migliaccio G, Simons K. Palmitylation of viral membrane glycoproteins takes place after exit from the endoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem. 1989;264:12590–12595. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

