Pre-M phase-promoting factor associates with annulate lamellae in Xenopus oocytes and egg extracts
- PMID: 12631728
- PMCID: PMC151584
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e02-08-0511
Pre-M phase-promoting factor associates with annulate lamellae in Xenopus oocytes and egg extracts
Abstract
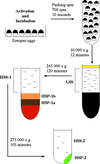
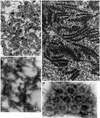
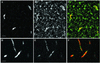
We have used complementary biochemical and in vivo approaches to study the compartmentalization of M phase-promoting factor (MPF) in prophase Xenopus eggs and oocytes. We first examined the distribution of MPF (Cdc2/CyclinB2) and membranous organelles in high-speed extracts of Xenopus eggs made during mitotic prophase. These extracts were found to lack mitochondria, Golgi membranes, and most endoplasmic reticulum (ER) but to contain the bulk of the pre-MPF pool. This pre-MPF could be pelleted by further centrifugation along with components necessary to activate it. On activation, Cdc2/CyclinB2 moved into the soluble fraction. Electron microscopy and Western blot analysis showed that the pre-MPF pellet contained a specific ER subdomain comprising "annulate lamellae" (AL): stacked ER membranes highly enriched in nuclear pores. Colocalization of pre-MPF with AL was demonstrated by anti-CyclinB2 immunofluorescence in prophase oocytes, in which AL are positioned close to the vegetal surface. Green fluorescent protein-CyclinB2 expressed in oocytes also localized at AL. These data suggest that inactive MPF associates with nuclear envelope components just before activation. This association may explain why nuclei and centrosomes stimulate MPF activation and provide a mechanism for targeting of MPF to some of its key substrates.
Figures




References
-
- Alfa CE, Ducommun B, Beach D, Hyams JS. Distinct nuclear and spindle pole body population of cyclin-cdc2 in fission yeast. Nature. 1990;347:680–682. - PubMed
-
- Argon Y, Simen BB. GRP94, an ER chaperone with protein and peptide binding properties. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 1999;10:495–505. - PubMed
-
- Ashcroft NR, Srayko M, Kosinski ME, Mains PE, Golden A. RNA-Mediated interference of a cdc25 homolog in Caenorhabditis elegans results in defects in the embryonic cortical membrane, meiosis, and mitosis. Dev Biol. 1999;206:15–32. - PubMed
-
- Audit M, Barbier M, Soyer-Gobillard MO, Albert M, Géraud ML, Nicolas G, Lenaers G. CyclinB (p56cdc13) localization in yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe: an ultrastructural and immunocytochemical study. Biol Cell. 1996;86:1–10. - PubMed
-
- Bagley S, Goldberg MW, Cronshaw JM, Rutherford S, Allen TD. The nuclear pore complex. J Cell Sci. 2000;113:3885–3886. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

