Obscurin is a ligand for small ankyrin 1 in skeletal muscle
- PMID: 12631729
- PMCID: PMC151585
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e02-07-0411
Obscurin is a ligand for small ankyrin 1 in skeletal muscle
Abstract
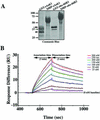
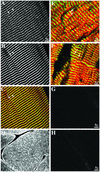
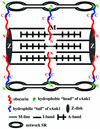
The factors that organize the internal membranes of cells are still poorly understood. We have been addressing this question using striated muscle cells, which have regular arrays of membranes that associate with the contractile apparatus in stereotypic patterns. Here we examine links between contractile structures and the sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) established by small ankyrin 1 (sAnk1), a approximately 17.5-kDa integral protein of network SR. We used yeast two-hybrid to identify obscurin, a giant Rho-GEF protein, as the major cytoplasmic ligand for sAnk1. The binding of obscurin to the cytoplasmic sequence of sAnk1 is mediated by a sequence of obscurin that is C-terminal to its last Ig-like domain. Binding was confirmed in two in vitro assays. In one, GST-obscurin, bound to glutathione-matrix, specifically adsorbed native sAnk1 from muscle homogenates. In the second, MBP-obscurin bound recombinant GST-sAnk1 in nitrocellulose blots. Kinetic studies using surface plasmon resonance yielded a K(D) = 130 nM. On subcellular fractionation, obscurin was concentrated in the myofibrillar fraction, consistent with its identification as sarcomeric protein. Nevertheless, obscurin, like sAnk1, concentrated around Z-disks and M-lines of striated muscle. Our findings suggest that obscurin binds sAnk1, and are the first to document a specific and direct interaction between proteins of the sarcomere and the SR.
Figures





References
-
- Bang ML, et al. The complete gene sequence of titin, expression of an unusual approximately 700-kDa titin isoform, and its interaction with obscurin identify a novel Z-line to I-band linking system. Circ Res. 2001;89:1065–1072. - PubMed
-
- Baumann O, Walz B. Endoplasmic reticulum of animal cells and its organization into structural and functional domains. Int Rev Cytol. 2001;205:149–214. - PubMed
-
- Bennett V. Ankyrins. Adaptors between diverse plasma membrane proteins and the cytoplasm. J Biol Chem. 1992;267:8703–8706. - PubMed
-
- Bennett V, Chen L. Ankyrins and cellular targeting of diverse membrane proteins to physiological sites. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2001;13:61–67. - PubMed
-
- Birkenmeier CS, White RA, Peters LL, Hall EJ, Lux SE, Barker JE. Complex patterns of sequence variation and multiple 5′ and 3′ ends are found among transcripts of the erythroid ankyrin gene. J Biol Chem. 1993;81:2144–2149. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

