Importin-alpha mediates the regulated nuclear targeting of serum- and glucocorticoid-inducible protein kinase (Sgk) by recognition of a nuclear localization signal in the kinase central domain
- PMID: 12631736
- PMCID: PMC151592
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e02-03-0170
Importin-alpha mediates the regulated nuclear targeting of serum- and glucocorticoid-inducible protein kinase (Sgk) by recognition of a nuclear localization signal in the kinase central domain
Abstract
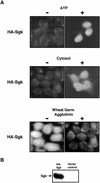
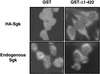
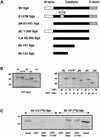
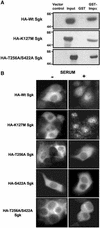
The transcriptionally regulated serum and glucocorticoid inducible protein kinase (Sgk) is localized to the nucleus in a serum-dependent manner, and a yeast two-hybrid genetic screen uncovered a specific interaction between Sgk and the importin-alpha nuclear import receptor. In vitro GST pull down assays demonstrated a strong and direct association of importin-alpha with endogenous Sgk and exogenously expressed HA-tagged Sgk, whereas both components coimmunoprecipitate and colocalize to the nucleus after serum stimulation. Consistent with an active mechanism of nuclear localization, the nuclear import of HA-Sgk in permeabilized cells required ATP, cytoplasm, and a functional nuclear pore complex. Ectopic addition of a 107 amino acid carboxy-terminal fragment of importin-alpha, which contains the Sgk binding region, competitively inhibited the ability of endogenous importin-alpha to import Sgk into nuclei in vitro. Mutagenesis of lysines by alanine substitution defined a KKAILKKKEEK sequence within the central domain of Sgk between amino acids 131-141 that functions as a nuclear localization signal (NLS) required for the in vitro interaction with importin-alpha and for nuclear import of full-length Sgk in cultured cells. The serum-induced nuclear import of Sgk requires the NLS-dependent recognition of Sgk by importin-alpha as well as the PI3-kinase-dependent phosphorylation of Sgk. Our results define a new role importin-alpha in the stimulus-dependent control of signal transduction by nuclear localized protein kinases.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The stimulus-dependent co-localization of serum- and glucocorticoid-regulated protein kinase (Sgk) and Erk/MAPK in mammary tumor cells involves the mutual interaction with the importin-alpha nuclear import protein.Exp Cell Res. 2007 Sep 10;313(15):3261-75. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2007.07.009. Epub 2007 Jul 19. Exp Cell Res. 2007. PMID: 17692313 Free PMC article.
-
Stimulus-dependent regulation of serum and glucocorticoid inducible protein kinase (SGK) transcription, subcellular localization and enzymatic activity.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2003;13(1):1-12. doi: 10.1159/000070244. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2003. PMID: 12649597 Review.
-
The importin-beta binding domain of snurportin1 is responsible for the Ran- and energy-independent nuclear import of spliceosomal U snRNPs in vitro.J Cell Biol. 2002 Feb 4;156(3):467-79. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200108114. Epub 2002 Jan 28. J Cell Biol. 2002. PMID: 11815630 Free PMC article.
-
AMP-activated protein kinase-regulated phosphorylation and acetylation of importin alpha1: involvement in the nuclear import of RNA-binding protein HuR.J Biol Chem. 2004 Nov 12;279(46):48376-88. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M409014200. Epub 2004 Sep 1. J Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 15342649
-
Classical nuclear localization signals: definition, function, and interaction with importin alpha.J Biol Chem. 2007 Feb 23;282(8):5101-5. doi: 10.1074/jbc.R600026200. Epub 2006 Dec 14. J Biol Chem. 2007. PMID: 17170104 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The functional role of the novel biomarker karyopherin α 2 (KPNA2) in cancer.Cancer Lett. 2013 Apr 30;331(1):18-23. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2012.12.013. Epub 2012 Dec 23. Cancer Lett. 2013. PMID: 23268335 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cytotoxicity, anti-angiogenic, apoptotic effects and transcript profiling of a naturally occurring naphthyl butenone, guieranone A.Cell Div. 2012 Jun 20;7(1):16. doi: 10.1186/1747-1028-7-16. Cell Div. 2012. PMID: 22892065 Free PMC article.
-
The N-terminus of the serum- and glucocorticoid-inducible kinase Sgk1 specifies mitochondrial localization and rapid turnover.Biochem J. 2006 Oct 1;399(1):69-76. doi: 10.1042/BJ20060386. Biochem J. 2006. PMID: 16776652 Free PMC article.
-
SGK1 in Human Cancer: Emerging Roles and Mechanisms.Front Oncol. 2021 Jan 19;10:608722. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.608722. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33542904 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of serum/glucocorticoid-regulated kinase 1 in brain function following cerebral ischemia.J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2024 Jul;44(7):1145-1162. doi: 10.1177/0271678X231224508. Epub 2024 Jan 18. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2024. PMID: 38235747 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alliston TN, Gonzalez-Robayna IJ, Buse P, Firestone GL, Richards JS. Expression and localization of serum/glucocorticoid-induced kinase in the rat ovary: relation to follicular growth and differentiation. Endocrinology. 2000;141:385–395. - PubMed
-
- Alliston TN, Maiyar AC, Buse P, Firestone GL, Richards JS. Follicle stimulating hormone-regulated expression of serum/glucocorticoid-inducible kinase in rat ovarian granulosa cells: a functional role for the Sp1 family in promoter activity. Mol Endocrinol. 1997;11:1934–1949. - PubMed
-
- Alvarez de la Rosa D, Zhang P, Naray-Fejes-Toth A, Fejes-Toth G, Canessa CM. The serum and glucocorticoid kinase sgk increases the abundance of epithelial sodium channels in the plasma membrane of Xenopus oocytes. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:37834–37839. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

