Functional somatotopy of finger representations in human primary motor cortex
- PMID: 12632465
- PMCID: PMC6872002
- DOI: 10.1002/hbm.10084
Functional somatotopy of finger representations in human primary motor cortex
Abstract
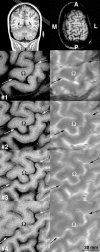
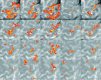
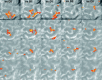
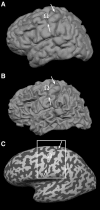
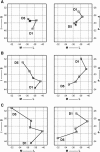
To assess the degree of fine-scale somatotopy within the hand area of the human primary motor cortex (M1), functional mapping of individual movements of all fingers was performed in healthy young subjects (n = 7) using MRI at 0.8 x 0.8 mm2 resolution and 4 mm section thickness. The experimental design comprised both a direct paradigm contrasting single digit movements vs. motor rest and multiple differential paradigms contrasting single digit movements vs. the movement of another digit. Direct mapping resulted in largely overlapping activations. A somatotopic arrangement was only recognizable when considering the mean center-of-mass coordinates of individual digit representations averaged across subjects. In contrast, differential paradigms revealed more segregated and somatotopically ordered activations in single subjects. The use of center-of-mass coordinates yielded inter-digit distances ranging from 2.0 to 16.8 mm, which reached statistical significance for pairs of more distant digits. For the middle fingers, the functional somatotopy obtained by differential mapping was dependent on the choice of the digit used for control. These results confirm previous concepts that finger somatotopy in the human M1 hand area emerges as a functional predominance of individual digit representations sharing common areas in a distributed though ordered network.
Copyright 2003 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures



References
-
- Beisteiner R, Windischberger C, Lanzenberger R, Edward V, Cunnington R, Erdler M, Gartus A, Streibl B, Moser E, Deecke L (2001): Finger somatotopy in human motor cortex. Neuroimage 13: 1016–1026. - PubMed
-
- Dechent P, Frahm J (2000): Direct mapping of ocular dominance columns in human primary visual cortex. Neuroreport 11: 3247–3249. - PubMed
-
- Donoghue JP, Leibovic S, Sanes JN (1992): Organization of the forelimb area in squirrel monkey motor cortex: representation of digit, wrist, and elbow muscles. Exp Brain Res 89: 1–19. - PubMed
-
- Ferrier D. Experiments on the brain of monkeys. (1875): Proc R Soc London 23: 409–430.
-
- Foerster O (1936): The motor cortex of man in the light of Hughlings Jackson's doctrines. Brain 59: 135–159.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

