Analysis of gene expression profile induced by EMP-1 in esophageal cancer cells using cDNA Microarray
- PMID: 12632483
- PMCID: PMC4621547
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v9.i3.392
Analysis of gene expression profile induced by EMP-1 in esophageal cancer cells using cDNA Microarray
Abstract
Aim: To obtain human esophageal cancer cell EC9706 stably expressed epithelial membrane protein-1 (EMP-1) with integrated eukaryotic plasmid harboring the open reading frame (ORF) of human EMP-1, and then to study the mechanism by which EMP-1 exerts its diverse cellular action on cell proliferation and altered gene profile by exploring the effect of EMP-1.
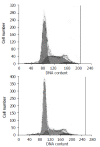
Methods: The authors first constructed pcDNA3.1/myc-his expression vector harboring the ORF of EMP-1 and then transfected it into human esophageal carcinoma cell line EC9706. The positive clones were analyzed by Western blot and RT-PCR. Moreover, the cell growth curve was observed and the cell cycle was checked by FACS technique. Using cDNA microarray technology, the authors compared the gene expression pattern in positive clones with control. To confirm the gene expression profile, semi-quantitative RT-PCR was carried out for 4 of the randomly picked differentially expressed genes. For those differentially expressed genes, classification was performed according to their function and cellular component.
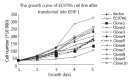
Results: Human EMP-1 gene can be stably expressed in EC9706 cell line transfected with human EMP-1. The authors found the cell growth decreased, among which S phase was arrested and G1 phase was prolonged in the transfected positive clones. By cDNA microarray analysis, 35 genes showed an over 2.0 fold change in expression level after transfection, with 28 genes being consistently up-regulated and 7 genes being down-regulated. Among the classified genes, almost half of the induced genes (13 out of 28 genes) were related to cell signaling, cell communication and particularly to adhesion.
Conclusion: Overexpression of human EMP-1 gene can inhibit the proliferation of EC9706 cell with S phase arrested and G1 phase prolonged. The cDNA microarray analysis suggested that EMP-1 may be one of regulators involved in cell signaling, cell communication and adhesion regulators.
Figures





References
-
- Gnirke AU, Weidle UH. Investigation of prevalence and regulation of expression of progression associated protein (PAP) Anticancer Res. 1998;18:4363–4369. - PubMed
-
- Taylor V, Welcher AA, Program AE, Suter U. Epithelial membrane protein-1, peripheral myelin protein 22, and lens membrane protein 20 define a novel gene family. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:28824–28833. - PubMed
-
- Chen Y, Medvedev A, Ruzanov P, Marvin KW, Jetten AM. cDNA cloning, genomic structure, and chromosome mapping of the human epithelial membrane protein CL-20 gene (EMP1), a member of the PMP22 family. Genomics. 1997;41:40–48. - PubMed
-
- Lobsiger CS, Magyar JP, Taylor V, Wulf P, Welcher AA, Program AE, Suter U. Identification and characterization of a cDNA and the structural gene encoding the mouse epithelial membrane protein-1. Genomics. 1996;36:379–387. - PubMed
-
- Taylor V, Suter U. Epithelial membrane protein-2 and epithelial membrane protein-3: two novel members of the peripheral myelin protein 22 gene family. Gene. 1996;175:115–120. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

