Resveratrol induces apoptosis in human esophageal carcinoma cells
- PMID: 12632486
- PMCID: PMC4621550
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v9.i3.408
Resveratrol induces apoptosis in human esophageal carcinoma cells
Abstract
Aim: To investigate the apoptosis in esophageal cancer cells induced by resveratrol, and the relation between this apoptosis and expression of Bcl-2 and Bax.
Methods: In in vitro experiments, MTT assay was used to determine the cell growth inhibitory rate. Transmission electron microscope and TUNEL staining method were used to quantitatively and qualitively detect the apoptosis status of esophageal cancer cell line EC-9706 before and after the resveratrol treatment. Immunohistochemical staining was used to detect the expression of apoptosis-regulated gene Bcl-2 and Bax.
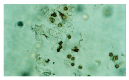
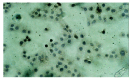
Results: Resveratrol inhibited the growth of esophageal cancer cell line EC-9706 in a dose-and time-dependent manner. Resveratrol induced EC-9706 cells to undergo apoptosis with typically apoptotic characteristics, including morphological changes of chromatin condensation, chromatin crescent formation, nucleus fragmentation and apoptotic body formation. TUNEL assay showed that after the treatment of EC-9706 cells with resveratrol (10 mmol/L) for 24 to 96 hours, the AIs were apparently increased with treated time (P<0.05). Immunohistochemical staining showed that after the treatment of EC-9706 cells with resveratrol (10 mmol/L) for 24 to 96 hours, the PRs of Bcl-2 proteins were apparently reduced with treated time (P<0.05) and the PRs of Bax proteins were apparently increased with treated time (P<0.05).
Conclusion: Resveratrol is able to induce the apoptosis in esophageal cancer. This apoptosis may be mediated by down-regulating the apoptosis-regulated gene Bcl-2 and up-regulating the expression of apoptosis-regulated gene bax.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Paclitaxel induces apoptosis in human gastric carcinoma cells.World J Gastroenterol. 2003 Mar;9(3):442-5. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v9.i3.442. World J Gastroenterol. 2003. PMID: 12632493 Free PMC article.
-
[Study on the molecular mechanism of apoptosis in esophageal cancer cells induced by soybean isoflavone].Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi. 2003 Nov;24(11):1040-3. Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi. 2003. PMID: 14687509 Chinese.
-
Anticancer activity of resveratrol on implanted human primary gastric carcinoma cells in nude mice.World J Gastroenterol. 2005 Jan 14;11(2):280-4. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i2.280. World J Gastroenterol. 2005. PMID: 15633232 Free PMC article.
-
[Inhibitory effect of resveratrol on the growth of human colon cancer ls174t cells and its subcutaneously transplanted tumor in nude mice and the mechanism of action].Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2009 Jan;31(1):15-9. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2009. PMID: 19538862 Chinese.
-
Apoptosis of human primary gastric carcinoma cells induced by genistein.World J Gastroenterol. 2004 Jun 15;10(12):1822-5. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v10.i12.1822. World J Gastroenterol. 2004. PMID: 15188515 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Inhibition of DNA primase and induction of apoptosis by 3,3'-diethyl-9-methylthia-carbocyanine iodide in hepatocellular carcinoma BEL-7402 cells.World J Gastroenterol. 2004 Feb 15;10(4):514-20. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v10.i4.514. World J Gastroenterol. 2004. PMID: 14966908 Free PMC article.
-
Natural Polyphenols in Cancer Management: Promising Role, Mechanisms, and Chemistry.Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2024;25(6):694-712. doi: 10.2174/1389201024666230822090318. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 37608669 Review.
-
Metabolic engineering of yeast and plants for the production of the biologically active hydroxystilbene, resveratrol.J Biomed Biotechnol. 2012;2012:579089. doi: 10.1155/2012/579089. Epub 2012 May 13. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2012. PMID: 22654481 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Resveratrol induces human K562 cell apoptosis, erythroid differentiation, and autophagy.Tumour Biol. 2014 Jun;35(6):5381-8. doi: 10.1007/s13277-014-1701-y. Epub 2014 Feb 15. Tumour Biol. 2014. PMID: 24526417
-
Dose-dependency of resveratrol in providing health benefits.Dose Response. 2010 Mar 18;8(4):478-500. doi: 10.2203/dose-response.09-015.Mukherjee. Dose Response. 2010. PMID: 21191486 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yoon SH, Kim YS, Ghim SY, Song BH, Bae YS. Inhibition of protein kinase CKII activity by resveratrol, a natural compound in red wine and grapes. Life Sci. 2002;71:2145–2152. - PubMed
-
- Gao X, Xu YX, Divine G, Janakiraman N, Chapman RA, Gautam SC. Disparate in vitro and in vivo antileukemic effects of resveratrol, a natural polyphenolic compound found in grapes. J Nutr. 2002;132:2076–2081. - PubMed
-
- Bhat KP, Pezzuto JM. Cancer chemopreventive activity of resveratrol. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2002;957:210–229. - PubMed
-
- Kuwajerwala N, Cifuentes E, Gautam S, Menon M, Barrack ER, Reddy GP. Resveratrol induces prostate cancer cell entry into s phase and inhibits DNA synthesis. Cancer Res. 2002;62:2488–2492. - PubMed
-
- Joe AK, Liu H, Suzui M, Vural ME, Xiao D, Weinstein IB. Resveratrol induces growth inhibition, S-phase arrest, apoptosis, and changes in biomarker expression in several human cancer cell lines. Clin Cancer Res. 2002;8:893–903. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials