Human coronavirus 229E: receptor binding domain and neutralization by soluble receptor at 37 degrees C
- PMID: 12634402
- PMCID: PMC150646
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.77.7.4435-4438.2003
Human coronavirus 229E: receptor binding domain and neutralization by soluble receptor at 37 degrees C
Abstract
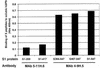
Truncated human coronavirus HCoV-229E spike glycoproteins containing amino acids 407 to 547 bound to purified, soluble virus receptor, human aminopeptidase N (hAPN). Soluble hAPN neutralized the infectivity of HCoV-229E virions at 37 degrees C, but not 4 degrees C. Binding of hAPN may therefore trigger conformational changes in the viral spike protein at 37 degrees C that facilitate virus entry.
Figures
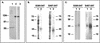

References
-
- Ashmun, R. A., and A. T. Look. 1990. Metalloprotease activity of CD13/aminopeptidase N on the surface of human myeloid cells. Blood 75:462-469. - PubMed
-
- Cavanagh, D. 1995. The coronavirus surface glycoprotein, p. 73-113. In S. G. Siddell (ed.), The Coronaviridae. Plenum Press, New York, N.Y.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

