Demonstration of functional coupling between gamma -aminobutyric acid (GABA) synthesis and vesicular GABA transport into synaptic vesicles
- PMID: 12634427
- PMCID: PMC153086
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0730698100
Demonstration of functional coupling between gamma -aminobutyric acid (GABA) synthesis and vesicular GABA transport into synaptic vesicles
Abstract
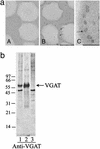
l-Glutamic acid decarboxylase (GAD) exists as both membrane-associated and soluble forms in the mammalian brain. Here, we propose that there is a functional and structural coupling between the synthesis of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) by membrane-associated GAD and its packaging into synaptic vesicles (SVs) by vesicular GABA transporter (VGAT). This notion is supported by the following observations. First, newly synthesized [(3)H]GABA from [(3)H]l-glutamate by membrane-associated GAD is taken up preferentially over preexisting GABA by using immunoaffinity-purified GABAergic SVs. Second, the activity of SV-associated GAD and VGAT seems to be coupled because inhibition of GAD also decreases VGAT activity. Third, VGAT and SV-associated Ca(2+)calmodulin-dependent kinase II have been found to form a protein complex with GAD. A model is also proposed to link the neuronal stimulation to enhanced synthesis and packaging of GABA into SVs.
Figures
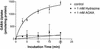
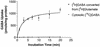

References
-
- Erlander M G, Tobin A J. Neurochem Res. 1991;16:215–226. - PubMed
-
- Dirkx R, Jr, Thomas A, Li L S, Lernmark Å, Sherwin R S, De Camilli P, Solimena M. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:2241–2246. - PubMed
-
- Sheikh S N, Martin D L. J Neurochem. 1996;66:2082–2090. - PubMed
-
- Kanaani J, Lissin D, Kash S F, Baekkekov S. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:37200–37209. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

