Combined analysis of genome scans of dutch and finnish families reveals a susceptibility locus for high-density lipoprotein cholesterol on chromosome 16q
- PMID: 12638083
- PMCID: PMC1180353
- DOI: 10.1086/374177
Combined analysis of genome scans of dutch and finnish families reveals a susceptibility locus for high-density lipoprotein cholesterol on chromosome 16q
Abstract
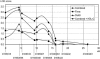
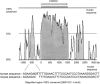
Several genomewide screens have been performed to identify novel loci predisposing to unfavorable serum lipid levels and coronary heart disease (CHD). We hypothesized that the accumulating data of these screens in different study populations could be combined to verify which of the identified loci truly harbor susceptibility genes. The power of this strategy has recently been demonstrated with other complex diseases, such as inflammatory bowel disease and asthma. We assessed the largely unknown genetic background of CHD by investigating the most common dyslipidemia predisposing to CHD, familial combined hyperlipidemia (FCHL), affecting 1%-2% of Western populations and 10%-20% of families with premature CHD. To be able to perform a combined data analysis, we unified the diagnostic criteria for FCHL and its component traits and combined the data from two genomewide scans performed in two populations, the Finns and the Dutch. As a result of our pooled data analysis, we identified three chromosomal regions, on chromosomes 2p25.1, 9p23, and 16q24.1, exceeding the statistical significance level of a LOD score >2.0. The 2p25.1 region was detected for the FCHL trait, and the 9p23 and 16q24.1 regions were detected for the low high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) trait. In addition, the previously recognized 1q21 region also obtained additional support in the other study sample, when the triglyceride trait was used. Analysis of the 16q24.1 region resulted in a statistically significant LOD score of 3.6 when the data from Finnish families with low HDL-C were included in the analysis. To search for the underlying gene in the 16q24.1 region, we investigated a novel functional and positional candidate gene, helix/forkhead transcription factor (FOXC2), by sequencing and by genotyping of two single-nucleotide polymorphisms in the families.
Figures

References
Electronic-Database Information
-
- Celera, http://www.celera.com
-
- Center for Medical Genetics, Marshfield Medical Research Foundation, http://research.marshfieldclinic.org/genetics/
-
- dbSNP Home Page, http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/SNP/
-
- Integrated DNA Technologies, http://www.idtdna.com/ (for Oligo Analyzer 2.5)
References
-
- Allayee A, Krass KL, Pajukanta P, Cantor RM, van der Kallen CJH, Mar R, Rotter JI, de Bruin TWA, Peltonen L, Lusis AJ (2002) Locus for elevated apolipoprotein b levels on chromosome 1p31 in families with familial combined hyperlipidemia. Circ Res 90:926–931 - PubMed
-
- Aouizerat BE, Allayee H, Cantor RM, Dallinga-Thie GM, Lanning CD, de Bruin TWA, Lusis AJ, Rotter JI (1999a) Linkage of a candidate gene locus to familial combined hyperlipidemia: lecithin:cholesterol acyltransferase on 16q. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 19:2730–2736 - PubMed
-
- Broeckel U, Hengstenberg C, Mayer B, Holmer S, Martin LJ, Comuzzie AG, Blangero J, Nurnberg P, Reis A, Riegger GA, Jacob HJ, Schunkert H (2002) A comprehensive linkage analysis for myocardial infarction and its related risk factors. Nat Genet 30:210–214 - PubMed
-
- Brunzell JD, Albers JJ, Chait A, Grundy SM, Groszek E, McDonald GB (1983) Plasma lipoproteins in familial combined hyperlipidemia and monogenic familial hypertriglyceridemia. J Lipid Res 24:147–155 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

