Prostaglandins but not nitric oxide protect renal medullary perfusion in anaesthetised rats receiving angiotensin II
- PMID: 12640010
- PMCID: PMC2342881
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2002.038075
Prostaglandins but not nitric oxide protect renal medullary perfusion in anaesthetised rats receiving angiotensin II
Abstract
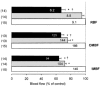
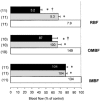
Angiotensin II (Ang II) fails to constrict renal medullary vasculature, possibly due to the counteraction of local vasodilators, such as prostaglandins or nitric oxide (NO). The effects of exogenous Ang II on intrarenal circulation were determined in anaesthetised rats that were untreated or pretreated with indomethacin (Indo) or L-NAME. The total renal blood flow (RBF), representing cortical perfusion, and outer and inner medullary blood flow (OMBF and IMBF) were measured. In untreated rats, Ang II decreased RBF in a dose dependent manner. Intravenous administration of 30 ng kg-1 min-1 Ang II decreased RBF by 38 % and OMBF by 9 % (both significant); IMBF was unaffected. Indo (5 mg kg-1 I.V.) significantly and similarly decreased OMBF and IMBF without affecting RBF. Ang II decreased IMBF by 27 % in Indo-pretreated rats, but caused no change in rats without pretreatment. The decreases in OMBF and RBF were comparable with or without Indo pretreatment. Inhibition of NO synthesis with L-NAME (0.6 mg kg-1 I.V.) significantly decreased RBF, OMBF and IMBF. Ang II infusion into L-NAME-pretreated rats induced a further significant decrease in RBF and OMBF without changing IMBF. We conclude that within the inner medulla, but not the outer medulla or cortex, prostaglandins effectively counteract the vasopressor effect of circulating Ang II.
Figures


References
-
- Arendshorst WJ, Brännström K, Ruan X. Action of angiotensin II on the renal microvasculature. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1999;10:S149–S161. - PubMed
-
- Bergström G, Evans RG. Integrative aspects of the renal medullary circulation. In: Anderson WP, Evans RG, Stevenson KM, editors. The Renal Circulation. Stanford, CT, USA: JAI Press Inc.; 2000. pp. 235–253.
-
- Edwards A, Silldorff EP, Pallone TL. The renal medullary microcirculation. Front Biosci. 2000;5:E36–52. - PubMed
-
- Heyman SN, Rosen S, Brezis M. The renal medulla: life at the edge of anoxia. Blood Purif. 1997;15:232–242. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

