Negative regulation of BRCA1 gene expression by HMGA1 proteins accounts for the reduced BRCA1 protein levels in sporadic breast carcinoma
- PMID: 12640109
- PMCID: PMC150734
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.23.7.2225-2238.2003
Negative regulation of BRCA1 gene expression by HMGA1 proteins accounts for the reduced BRCA1 protein levels in sporadic breast carcinoma
Abstract
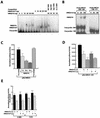
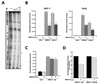
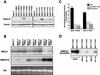
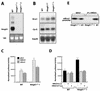
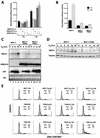
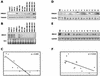
A drastic reduction in BRCA1 gene expression is a characteristic feature of aggressive sporadic breast carcinoma. However, the mechanisms underlying BRCA1 downregulation in breast cancer are not well understood. Here we report that both in vitro and in vivo HMGA1b protein binds to and inhibits the activity of both human and mouse BRCA1 promoters. Consistently, murine embryonic stem (ES) cells with the Hmga1 gene deleted display higher Brca1 mRNA and protein levels than do wild-type ES cells. Stable transfection of MCF-7 cells with the HMGA1b cDNA results in a decrease of BRCA1 gene expression and in a lack of BRCA1 induction after estrogen treatment. Finally, we found an inverse correlation between HMGA1 and BRCA1 mRNA and protein expression in human mammary carcinoma cell lines and tissues. These data indicate that HMGA1 proteins are involved in transcriptional regulation of the BRCA1 gene, and their overexpression may have a role in BRCA1 downregulation observed in aggressive mammary carcinomas.
Figures
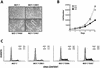
References
-
- Abe, N., T. Watanabe, M. Sugiyama, H. Uchimura, G. Chiappetta, A. Fusco, and Y. Atomi. 1999. Determination of high mobility group I(Y) expression level in colorectal neoplasias: a potential diagnostic marker. Cancer Res. 59:1169-1174. - PubMed
-
- Abe, N., T. Watanabe, T. Masaki, T. Mori, M. Sugiyama, H. Uchimura, Y. Fujioka, G. Chiappetta, A. Fusco, and Y. Atomi. 2000. Pancreatic duct cell carcinomas express high levels of high mobility group I(Y) proteins. Cancer Res. 60:3117-3122. - PubMed
-
- Baldassarre, G., M. V. Barone, B. Belletti, C. Sandomenico, P. Bruni, S. Spiezia, A. Boccia, M. T. Vento, A. Romano, S. Pepe, A. Fusco, and G. Viglietto. 1999. Key role of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p27kip1 for embryonal carcinoma cell survival and differentiation. Oncogene 18:6241-6251. - PubMed
-
- Baldassarre, G., M. Fedele, S. Battista, A. Vecchione, A. J. Klein-Szanto, M. Santoro, T. A. Waldmann, N. Azimi, C. M. Croce, and A. Fusco. 2001. Onset of natural killer cell lymphomas in transgenic mice carrying a truncated HMGI-C gene by the chronic stimulation of the IL-2 and IL-15 pathway. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 98:7970-7975. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bandiera, A., D. Bonifacio, G. Manfioletti, F. Mantovani, A. Rustighi, F. Zanconati, A. Fusco, L. Di Bonito, and V. Giancotti. 1998. Expression of HMGI(Y) proteins in squamous intraepithelial and invasive lesions of the uterine cervix. Cancer Res. 58:426-431. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
