Amiodarone induced optic neuropathy
- PMID: 12642303
- PMCID: PMC1771608
- DOI: 10.1136/bjo.87.4.420
Amiodarone induced optic neuropathy
Abstract
Aim: To determine the clinical features of amiodarone induced optic neuropathy, which may help distinguish it from non-arteritic anterior ischaemic optic neuropathy.
Methods: Retrospective observational case series of patients diagnosed with amiodarone induced optic neuropathy at the neuro-ophthalmology service from March 1998 to February 2001. Amiodarone was discontinued after discussion with the patient's cardiologist. Visual acuity, colour vision, automated perimetry, and funduscopy were performed on initial and follow up examinations.
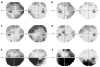
Results: Three patients with amiodarone induced optic neuropathy presented with mildly decreased vision, visual field defects, and bilateral optic disc swelling. Upon discontinuing the medication, visual function and optic disc swelling slowly improved in all three patients.
Conclusion: Amiodarone induced optic neuropathy can present with visual dysfunction, and is typically a bilateral process. Upon discontinuation of amiodarone, slow resolution of optic disc swelling occurs and visual function improves in some patients.
Figures

References
-
- American Heart Association. Guidelines 2000 for cardiopulmonary resuscitation and emergency cardiovascular care. Circulation 2000;102:I86–265. - PubMed
-
- Raeder EA, Podrid PJ, Lown B. Side effects and complications of amiodarone therapy. Am Heart J 1985;109:975–83. - PubMed
-
- Pollak PT. Clinical organ toxicity of antiarrhythmic compounds: ocular and pulmonary manifestions. Am J Cardiol 1999;84:37R–44R. - PubMed
-
- Mantyjarvi M, Tuppurainen K, Ikaheimo K. Ocular side effects of amiodarone. Surv Ophthalmol 1998;42:360–6. - PubMed
-
- Feiner LA, Younge BR, Kazmier FJ, et al. Optic neuropathy and amiodarone therapy. Mayo Clin Proc 1987;62:702–17. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
