Intravitreal triamcinolone acetonide for exudative age related macular degeneration
- PMID: 12642311
- PMCID: PMC1771586
- DOI: 10.1136/bjo.87.4.462
Intravitreal triamcinolone acetonide for exudative age related macular degeneration
Abstract
Aim: To evaluate the effect of intravitreal triamcinolone acetonide on the visual acuity of patients with exudative age related macular degeneration, to assess the duration of a possible effect, and to evaluate clinical side effects of the treatment.
Methods: The study included 67 patients (71 eyes) who presented with exudative age related macular degeneration of predominantly or total occult type (n = 68) or classic type (n = 3), and who received once, or repeatedly, an intravitreal injection of 25 mg of crystalline triamcinolone acetonide. Mean follow up time was 7.46 (SD 3.54) months (range 3.1-19.57 months).
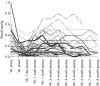
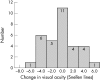
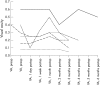
Results: Visual acuity increased significantly (p <0.001) from 0.16 (0.11) to a mean maximum of 0.23 (0.17). Postoperative visual acuity was highest 1-3 months after the injection. 47 (66.2%) eyes gained in maximal visual acuity and 11 (15.5%) eyes lost in visual acuity. Intraocular pressure increased significantly (p <0.001) from 15.1 (3.1) mm Hg at baseline to a maximal value of 23.0 (8.25) mm Hg. At the end of follow up, intraocular pressure again decreased significantly (p<0.001) to 16.8 (4.9) mm Hg. No cases of postoperative infectious endophthalmitis, rhegmatogenous retinal detachment, or proliferative vitreoretinopathy occurred. Owing to a decrease in visual acuity after an initial increase, six patients received a second intravitreal triamcinolone acetonide injection after which visual acuity increased again in three eyes.
Conclusions: Intravitreal injection of 25 mg of crystalline triamcinolone acetonide merits further study for the treatment of exudative age related macular degeneration.
Figures



References
-
- Bressler NM, Bressler SB, Fine SL. Age-related macular degeneration. Surv Ophthalmol 1988;32:375–413. - PubMed
-
- Mitchell P, Smith W, Attebo K, et al. Prevalence of age-related maculopathy in Australia. The Blue Mountains Eye Study. Ophthalmology 1995;102:1450–60. - PubMed
-
- Vingerling JR, Dielemans I, Hofman A, et al. The prevalence of age-related maculopathy in the Rotterdam Study. Ophthalmology 1995;102:205–10. - PubMed
-
- Schmidt-Erfurth U, Miller JW, Sickenberg M, et al. Photodynamic therapy with verteporfin for choroidal neovascularization caused by age-related macular degeneration: results of retreatments in a phase 1 and 2 study. Arch Ophthalmol 1999;117:1177–87. - PubMed
-
- Treatment of Age-related Macular Degeneration with Photodynamic Therapy (TAP) Study Group. Photodynamic therapy of subfoveal choroidal neovascularization in age-related macular degeneration with verteporfin: one-year results of 2 randomized clinical trials–TAP report. Arch Ophthalmol 1999;117:1329–45. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
