Experimental infection of North American birds with the New York 1999 strain of West Nile virus
- PMID: 12643825
- PMCID: PMC2958552
- DOI: 10.3201/eid0903.020628
Experimental infection of North American birds with the New York 1999 strain of West Nile virus
Abstract
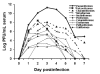
To evaluate transmission dynamics, we exposed 25 bird species to West Nile virus (WNV) by infectious mosquito bite. We monitored viremia titers, clinical outcome, WNV shedding (cloacal and oral), seroconversion, virus persistence in organs, and susceptibility to oral and contact transmission. Passeriform and charadriiform birds were more reservoir competent (a derivation of viremia data) than other species tested. The five most competent species were passerines: Blue Jay (Cyanocitta cristata), Common Grackle (Quiscalus quiscula), House Finch (Carpodacus mexicanus), American Crow (Corvus brachyrhynchos), and House Sparrow (Passer domesticus). Death occurred in eight species. Cloacal shedding of WNV was observed in 17 of 24 species, and oral shedding in 12 of 14 species. We observed contact transmission among four species and oral in five species. Persistent WNV infections were found in tissues of 16 surviving birds. Our observations shed light on transmission ecology of WNV and will benefit surveillance and control programs.
Figures


References
-
- Hayes CG. West Nile fever. In: Monath TP, editor. The arboviruses: epidemiology and ecology, Vol. V. Boca Raton (FL): CRC Press; 1989. p. 59–88.
-
- Asnis D, Conetta R, Waldman G, Teixeira A, McNamara T, Fine A, et al. Outbreak of West Nile-like viral encephalitis—New York, 1999. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 1999;48:845–9. - PubMed
-
- O’Leary DR, Nasci RS, Campbell GL, Marfin AA. West Nile virus activity—United States, 2001. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2002;51:497–501. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
