Human metapneumovirus in severe respiratory syncytial virus bronchiolitis
- PMID: 12643835
- PMCID: PMC2958536
- DOI: 10.3201/eid0903.020289
Human metapneumovirus in severe respiratory syncytial virus bronchiolitis
Abstract
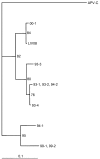
Reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction was used to detect segments of the M (matrix), N (nucleoprotein), and F (fusion) genes of human metapneumovirus in bronchoalveolar fluid from 30 infants with severe respiratory syncytial virus bronchiolitis. Seventy percent of them were coinfected with metapneumovirus. Such coinfection might be a factor influencing the severity of bronchiolitis.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical