Phosphoprotein with phosphoglycerate mutase activity from the archaeon Sulfolobus solfataricus
- PMID: 12644480
- PMCID: PMC151489
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.185.7.2112-2121.2003
Phosphoprotein with phosphoglycerate mutase activity from the archaeon Sulfolobus solfataricus
Abstract
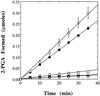
When soluble extracts of the extreme acidothermophilic archaeon Sulfolobus solfataricus were incubated with [gamma-(32)P]ATP, several proteins were radiolabeled. One of the more prominent of these, which migrated with a mass of approximately 46 kDa on sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE), was purified by column chromatography and SDS-PAGE and subjected to amino acid sequence analysis via both the Edman technique and mass spectroscopy. The best match to the partial sequence obtained was the potential polypeptide product of open reading frame sso0417, whose DNA-derived amino acid sequence displayed many features reminiscent of the 2,3-diphosphoglycerate-independent phosphoglycerate (PGA) mutases [iPGMs]. Open reading frame sso0417 was therefore cloned, and its protein product was expressed in Escherichia coli. Assays of its catalytic capabilities revealed that the protein was a moderately effective PGA mutase that also exhibited low levels of phosphohydrolase activity. PGA mutase activity was dependent upon the presence of divalent metal ions such as Co(2+) or Mn(2+). The recombinant protein underwent autophosphorylation when incubated with either [gamma-(32)P]ATP or [gamma-(32)P]GTP. The site of phosphorylation was identified as Ser(59), which corresponds to the catalytically essential serine residue in bacterial and eucaryal iPGMs. The phosphoenzyme intermediate behaved in a chemically and kinetically competent manner. Incubation of the (32)P-labeled phosphoenzyme with 3-PGA resulted in the disappearance of radioactive phosphate and the concomitant appearance of (32)P-labeled PGA at rates comparable to those measured in steady-state assays of PGA mutase activity.
Figures


References
-
- Amend, J. P., and E. L. Shock. 2001. Energetics of overall metabolic reactions of hyperthemophilic Archaea and bacteria. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 25:175-243. - PubMed
-
- Blattler, W. A., and J. R. Knowles. 1980. Phosphoglycerate mutases: stereochemical course of phosphoryl group transfers catalyzed by cofactor-dependent enzyme from rabbit muscle and cofactor-independent enzyme from wheat germ. Biochemistry 19:738-743. - PubMed
-
- Bradford, M. M. 1976. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 72:248-254. - PubMed
-
- Breathnach, R., and J. R. Knowles. 1977. Phosphoglycerate mutase from wheat germ: studies with 18O-labeled substrate, investigations of phosphatase and phosphoryl transfer activities, and evidence for a phosphoryl-enzyme intermediate. Biochemistry 16:3054-3060. - PubMed
-
- Britton, H. G., J. Carreras, and S. Grisolia. 1971. Mechanism of action of 2,3-diphosphoglycerate-independent phosphoglycerate mutase. Biochemistry 10:4522-4533. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

