Pto mutants differentially activate Prf-dependent, avrPto-independent resistance and gene-for-gene resistance
- PMID: 12644674
- PMCID: PMC166884
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.016113
Pto mutants differentially activate Prf-dependent, avrPto-independent resistance and gene-for-gene resistance
Abstract
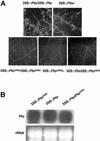
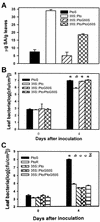
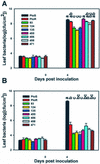
Pto confers disease resistance to Pseudomonas syringae pv tomato carrying the cognate avrPto gene. Overexpression of Pto under the cauliflower mosaic virus 35S promoter activates spontaneous lesions and confers disease resistance in tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum) plants in the absence of avrPto. Here, we show that these AvrPto-independent defenses require a functional Prf gene. Several Pto-interacting (Pti) proteins are thought to play a role in Pto-mediated defense pathways. To test if interactions with Pti proteins are required for the AvrPto-independent defense responses by Pto overexpression, we isolated several Pto mutants that were unable to interact with one or more Pti proteins, but retained normal interaction with AvrPto. Overexpression of two mutants, Pto(G50S) and Pto(R150S), failed to activate AvrPto-independent defense responses or confer enhanced resistance to the virulent P. s. pv tomato. When introduced into plants carrying 35S::Pto, 35S::Pto(G50S) dominantly suppressed the AvrPto-independent resistance caused by former transgene. 35S::Pto(G50S) also blocked the induction of a number of defense genes by the wild-type 35S::Pto. However, 35S::Pto(G50S) and 35S::Pto(R150S) plants were completely resistant to P. s. pv tomato (avrPto), indicating a normal gene-for-gene resistance. Furthermore, 35S::Pto(G50S) plants exhibited normal induction of defense genes in recognition of avrPto. Thus, the AvrPto-independent defense activation and gene-for-gene resistance mediated by Pto are functionally separable.
Figures



References
-
- Chang JH, Rathjen JP, Bernal AJ, Staskawicz BJ, Michelmore RW. avrPto Enhances Growth and Necrosis Caused by Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato in Tomato Lines Lacking Either Pto or Prf. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact. 2000;13:568–571. - PubMed
-
- Dangl JL, Jones JDG. Plant pathogens and integrated defence responses to infection. Nature. 2001;411:826–833. - PubMed
-
- He P, Warren RF, Shan L, Zhao T, Tang X, Zhou J-M. Overexpression of Pti5 potentiates pathogen-induced defense gene expression in tomato. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact. 2001;14:1453–1457. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

