mRNA of placental origin is readily detectable in maternal plasma
- PMID: 12644709
- PMCID: PMC153627
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0637450100
mRNA of placental origin is readily detectable in maternal plasma
Abstract
The discovery of circulating fetal nucleic acid in maternal plasma has opened up new possibilities for noninvasive prenatal diagnosis. Thus far, a gender- and polymorphism-independent fetal-specific target that can be used for prenatal screening and monitoring in all pregnant women has not been reported. In addition, the origin of such circulating nucleic acid has remained unclear. Here we provide direct evidence that the placenta is an important source of fetal nucleic acid release into maternal plasma by demonstrating that mRNA transcripts from placenta-expressed genes are readily detectable in maternal plasma. The surprising stability of such placental mRNA species in maternal plasma and their rapid clearance after delivery demonstrate that such circulating mRNA molecules are practical markers for clinical use. The measurement of such plasma mRNA markers has provided a gender-independent approach for noninvasive prenatal gene expression profiling and has opened up numerous research and diagnostic possibilities.
Figures
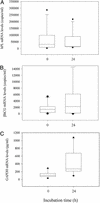
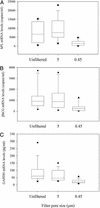
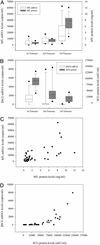
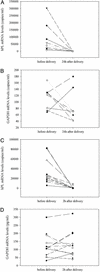
Comment in
-
Placental mRNA in maternal plasma: prospects for fetal screening.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003 Apr 15;100(8):4360-2. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0830966100. Epub 2003 Apr 7. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003. PMID: 12682290 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Nawroz H, Koch W, Anker P, Stroun M, Sidransky D. Nat Med. 1996;2:1035–1037. - PubMed
-
- Chen X Q, Stroun M, Magnenat J L, Nicod L P, Kurt A M, Lyautey J, Lederrey C, Anker P. Nat Med. 1996;2:1033–1035. - PubMed
-
- Lo Y M D, Corbetta N, Chamberlain P F, Rai V, Sargent I L, Redman C W, Wainscoat J S. Lancet. 1997;350:485–487. - PubMed
-
- Pertl B, Bianchi D W. Obstet Gynecol. 2001;98:483–490. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

